Spatially constrained incoherent motion method improves diffusion-weighted MRI signal decay analysis in the liver and spleen
- PMID: 25832079
- PMCID: PMC4376755
- DOI: 10.1118/1.4915495
Spatially constrained incoherent motion method improves diffusion-weighted MRI signal decay analysis in the liver and spleen
Abstract
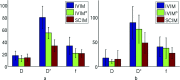
Purpose: To evaluate the effect of the spatially constrained incoherent motion (SCIM) method on improving the precision and robustness of fast and slow diffusion parameter estimates from diffusion-weighted MRI in liver and spleen in comparison to the independent voxel-wise intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model.
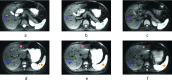
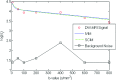
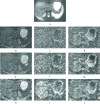
Methods: We collected diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI) data of 29 subjects (5 healthy subjects and 24 patients with Crohn's disease in the ileum). We evaluated parameters estimates' robustness against different combinations of b-values (i.e., 4 b-values and 7 b-values) by comparing the variance of the estimates obtained with the SCIM and the independent voxel-wise IVIM model. We also evaluated the improvement in the precision of parameter estimates by comparing the coefficient of variation (CV) of the SCIM parameter estimates to that of the IVIM.
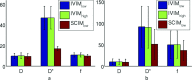
Results: The SCIM method was more robust compared to IVIM (up to 70% in liver and spleen) for different combinations of b-values. Also, the CV values of the parameter estimations using the SCIM method were significantly lower compared to repeated acquisition and signal averaging estimated using IVIM, especially for the fast diffusion parameter in liver (CVIV IM = 46.61 ± 11.22, CVSCIM = 16.85 ± 2.160, p < 0.001) and spleen (CVIV IM = 95.15 ± 19.82, CVSCIM = 52.55 ± 1.91, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The SCIM method characterizes fast and slow diffusion more precisely compared to the independent voxel-wise IVIM model fitting in the liver and spleen.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

