Orally administered moxifloxacin prolongs QTc in healthy Chinese volunteers: a randomized, single-blind, crossover study
- PMID: 25832425
- PMCID: PMC4387299
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2014.153
Orally administered moxifloxacin prolongs QTc in healthy Chinese volunteers: a randomized, single-blind, crossover study
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the QT/QTc effects of orally administered moxifloxacin in healthy Chinese volunteers.
Methods: This was a single-blinded, randomized, single-dose, placebo-controlled, two-period cross-over study. A total of 24 healthy Chinese volunteers were enrolled, randomly assigned to two groups: one group received moxifloxacin (400 mg, po) followed by placebo with a 7-d interval, another group received placebo followed by moxifloxacin with a 7-d interval. On the days of dosing, 12-lead 24 h Holter ECGs were recorded and evaluated by an ECG laboratory blind to the treatments. Blood samples were collected to determine plasma concentrations of moxifloxacin.
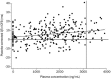
Results: The orally administered moxifloxacin significantly prolonged the mean QTc at all time points except 0.5 h post-dose. The largest time-matched difference in the QTcI was 8.35 ms (90% CI: 5.43, 11.27) at 4 h post-dose. The peak effect on QTcF was 9.35 ms (90% CI: 6.36, 12.34) at 3 h post-dose. A pharmacokinetic-QTc model suggested a 2.084 ms increase in the QTc interval for every 1000 ng/mL increase in plasma concentration of moxifloxacin. In addition, the orally administered moxifloxacin was well tolerated by the subjects.
Conclusion: Orally administered moxifloxacin significantly prolongs QTc, which supports its use as a positive control in ICH-E14 TQT studies in Chinese volunteers.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thorough QT study of the effect of oral moxifloxacin on QTc interval in the fed and fasted state in healthy Japanese and Caucasian subjects.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;77(1):170-9. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12168. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 23713767 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Population pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin and its concentration-QT interval relationship modeling in Chinese healthy volunteers.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 Nov;38(11):1580-1588. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.76. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017. PMID: 28713157 Free PMC article.
-
Moxifloxacin-induced QTc interval prolongations in healthy male Japanese and Caucasian volunteers: a direct comparison in a thorough QT study.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Sep;80(3):446-59. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12684. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26011050 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of nalmefene 20 and 80 mg on the corrected QT interval and T-wave morphology: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo- and moxifloxacin-controlled, single-centre study.Clin Drug Investig. 2011 Nov 1;31(11):799-811. doi: 10.1007/BF03256919. Clin Drug Investig. 2011. PMID: 21967071 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of sugammadex doses up to 32 mg/kg alone or in combination with rocuronium or vecuronium on QTc prolongation: a thorough QTc study.Clin Drug Investig. 2010;30(9):599-611. doi: 10.2165/11537210-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2010. PMID: 20568829 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Limited Sampling Strategies Using Linear Regression and the Bayesian Approach for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Moxifloxacin in Tuberculosis Patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Jun 24;63(7):e00384-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00384-19. Print 2019 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31010868 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of hyperglycaemia in combination with moxifloxacin on cardiac repolarization in male and female patients with type I diabetes.Clin Res Cardiol. 2022 Oct;111(10):1147-1160. doi: 10.1007/s00392-022-02037-8. Epub 2022 May 21. Clin Res Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35596784 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Establishing assay sensitivity in QT studies: experience with the use of moxifloxacin in an early phase clinical pharmacology study and comparison with its effect in a thorough QT study.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;71(12):1451-9. doi: 10.1007/s00228-015-1959-z. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26423621 Clinical Trial.
-
Moxifloxacin concentration correlate with QTc interval in rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis patients on shorter treatment regimens.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2022 Jun 6;28:100320. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2022.100320. eCollection 2022 Aug. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2022. PMID: 35706565 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of the Effect of Sevoflurane and Propofol on Ventricular Repolarisation after Preoperative Cefuroxime Infusion.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jan 2;2019:8978906. doi: 10.1155/2019/8978906. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30719450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yan GX, Lankipalli RS, Burke JF, Musco S, Kowey PR. Ventricular repolarization components on the electrocardiogram: cellular basis and clinical significance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:401–9. - PubMed
-
- Roden DM. Drug-induced prolongation of the QT interval. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1013–22. - PubMed
-
- Strnadova C. The assessment of QT/QTc interval prolongation in clinical trials: a regulatory perspective. Drug Information J. 2005;39:407–33.
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH). ICH topic E14. The clinical evaluation of QT/QTc interval prolongation and proarrhythmic potential for non-antiarrhythmic drugs (Step 4). 12 May 2005. Available from: http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/ Ef... (last accessed on 10 September 2012).
-
- E14 implementation working group: ICH E14 guideline: the clinical evaluation of QT/QTc interval prolongation and proarrhythmic potential for non-antiarrhythmic drugs questions & answers (R1). 5 April 2012. available from: http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/ Ef... (last accessed on 10 September 2012).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

