Transfer of the IL-37b gene elicits anti-tumor responses in mice bearing 4T1 breast cancer
- PMID: 25832432
- PMCID: PMC4387308
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2015.3
Transfer of the IL-37b gene elicits anti-tumor responses in mice bearing 4T1 breast cancer
Abstract
Aim: IL-37b has shown anti-cancer activities in addition to its anti-inflammatory properties. In this study, we investigated the effects of IL-37b on breast carcinoma growth in mice and to determine the involvement of T cell activation in the effects.
Methods: IL-37b gene was transferred into mouse breast carcinoma cell line 4T1 (4T1-IL37b cells), the expression of secretory IL-37b by the cells was detected, and the effects of IL-37b expression on the cell proliferation in vitro was evaluated. After injection of 4T1 cells or 4T1-IL37b cells into immunocompetent BALB/c mice, immunodeficient BALB/c nude mice and NOD-SCID mice, the tumor growth and survival rate were measured. The proliferation of T cells in vitro was also detected.
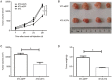
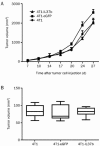
Results: IL-37b was detected in the supernatants of 4T1-IL37b cells with a concentration of 12.02 ± 0.875 ng/mL. IL-37b expression did not affect 4T1 cell proliferation in vitro. BALB/c mice inoculated with 4T1-IL37b cells showed significant retardation of tumor growth. BALB/c mice inoculated with both 4T1 cells and mitomycin C-treated 4T1-IL37b cells also showed significant retardation of tumor growth. But the anti-cancer activity of IL-37b was abrogated in BALB/c nude mice and NOD-SCID mice inoculated with 4T1-IL37b cells. Recombinant IL-37b slightly promoted CD4(+) T cell proliferation without affecting CD8(+) T cell proliferation.
Conclusion: IL-37b exerts anti-4T1 breast carcinoma effects in vivo by modulating the tumor microenvironment and influencing T cell activation.
Figures


References
-
- Boraschi D, Lucchesi D, Hainzl S, Leitner M, Maier E, Mangelberger D, et al. IL-37: a new anti-inflammatory cytokine of the IL-1 family. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2011;22:127–47. - PubMed
-
- Grimsby S, Jaensson H, Dubrovska A, Lomnytska M, Hellman U, Souchelnytskyi S. Proteomics-based identification of proteins interacting with Smad3: SREBP-2 forms a complex with Smad3 and inhibits its transcriptional activity. FEBS Lett. 2004;577:93–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

