Clinical heterogeneity of primary familial brain calcification due to a novel mutation in PDGFB
- PMID: 25832657
- PMCID: PMC4424129
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001517
Clinical heterogeneity of primary familial brain calcification due to a novel mutation in PDGFB
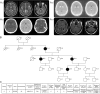
Figures
References
-
- Wang C, Li Y, Shi L, et al. Mutations in SLC20A2 link familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification with phosphate homeostasis. Nat Genet 2012;44:254–256. - PubMed
-
- Nicolas G, Pottier C, Maltete D, et al. Mutation of the PDGFRB gene as a cause of idiopathic basal ganglia calcification. Neurology 2013;80:181–187. - PubMed
-
- Keller A, Westenberger A, Sobrido MJ, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding PDGF-B cause brain calcifications in humans and mice. Nat Genet 2013;45:1077–1082. - PubMed
-
- Nicolas G, Rovelet-Lecrux A, Pottier C, et al. PDGFB partial deletion: a new, rare mechanism causing brain calcification with leukoencephalopathy. J Mol Neurosci 2014;53:171–175. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi T, Legati A, Nishikawa T, Coppola G. First Japanese family with primary familial brain calcification due to a mutation in the PDGFB gene: an exome analysis study. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2015;69:77–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
