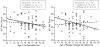Neuropsychological sex differences associated with age of initiated use among young adult cannabis users
- PMID: 25832823
- PMCID: PMC4441859
- DOI: 10.1080/13803395.2015.1020770
Neuropsychological sex differences associated with age of initiated use among young adult cannabis users
Abstract
Introduction: Earlier initiation of cannabis use is associated with poorer neuropsychological functioning across several domains. Given well-documented sex differences in neuromaturation during adolescence, initiation of cannabis use during this time may affect neuropsychological functioning differently for males and females.
Method: In the current study, we examined sex differences in the relationship between age of initiated cannabis use and neuropsychological performance after controlling for amount of lifetime cannabis use in 44 male and 25 female young adult cannabis users.
Results: We found that an earlier age of initiated use was related to poorer episodic memory, especially immediate recall, in females, but not in males. On the other hand, we found that, surprisingly, an earlier age of initiated use was associated with better decision making overall. However, exploratory analyses found sex-specific factors associated with decision making and age of initiated use, specifically that attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms in females may drive the relationship between an earlier age of initiated use and better decision making. Further, an earlier age of initiated use was associated with less education, a lower IQ, and fewer years of mother's education for females, but more lifetime cannabis use for males.
Conclusions: Taken together, our findings suggest there are sex differences in the associations between age of initiated cannabis use and neuropsychological functioning. The current study provides preliminary evidence that males and females may have different neuropsychological vulnerabilities that place them at risk for initiating cannabis use and continued cannabis use, highlighting the importance of examining the impact of cannabis on neuropsychological functioning separately for males and females.
Keywords: Cannabis; Cognition; Marijuana; Sex differences; THC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Battisti RA, Roodenrys S, Johnstone SJ, Pesa N, Hermens DF, Solowij N. Chronic cannabis users show altered neurophysiological functioning on Stroop task conflict resolution. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2010;212(4):613–624. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A. Iowa gambling task (IGT) professional manual. Lutz: Psychological Assessment Resources; 2007.
-
- Bechara A, Damasio AR, Damasio H, Anderson SW. Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition. 1994;50(1–3):7–15. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Brown G, Steer RA. Beck Depression Inventory II Manual. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation; 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources