Sustainable Efficacy of Switching From Intravenous to Subcutaneous Tocilizumab Monotherapy in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 25832859
- PMCID: PMC5054840
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.22598
Sustainable Efficacy of Switching From Intravenous to Subcutaneous Tocilizumab Monotherapy in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of switching from intravenous (IV) tocilizumab (TCZ) to subcutaneous (SC) TCZ monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Methods: Patients who had completed 24 weeks of TCZ-SC (162 mg/2 weeks) or TCZ-IV (8 mg/kg/4 weeks) monotherapy in the double-blind period of the MUSASHI study were enrolled in an 84-week open-label extension period. All received TCZ-SC (162 mg/2 weeks) monotherapy. Effects of the IV to SC switch were evaluated at week 36 (12 weeks after switching).
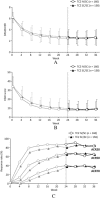
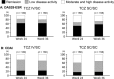
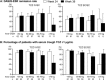
Results: Overall, 319 patients received ≥1 dose of TCZ-SC during the open-label extension period; 160 switched from TCZ-IV to TCZ-SC (TCZ IV/SC) and 159 continued TCZ-SC (TCZ SC/SC). Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using the erythrocyte sedimentation rate clinical remission rates were 62.5% (100 of 160) for TCZ IV/SC and 50.0% (79 of 158) for TCZ SC/SC at week 24, and were maintained at 62.5% (100 of 160) and 57.0% (90 of 158), respectively, at week 36. In the TCZ IV/SC group, 9% of patients (9 of 100) who had achieved remission at week 24 could not maintain remission at week 36. In TCZ IV/SC patients weighing ≥70 kg, the percentage with a sufficient serum TCZ concentration (≥1 μg/ml) decreased from 90.9% (10 of 11) at week 24 to 45.5% (5 of 11) at week 36. Overall safety profiles were similar in TCZ IV/SC and TCZ SC/SC except for mild injection site reactions in TCZ IV/SC.
Conclusion: Efficacy is adequately maintained in most patients switching from TCZ-IV (8 mg/kg/4 weeks) to TCZ-SC (162 mg/2 weeks) monotherapy. Patients receiving TCZ-IV can switch to TCZ-SC without serious safety concerns. Clinical efficacy may be reduced after switching in some patients with high body weight.
© 2015 The Authors. Arthritis Care & Research is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Komatsu N, Okamoto K, Sawa S, Nakashima T, Oh‐Hora M, Kodama T, et al. Pathogenic conversion of Foxp3 T cells into T17 cells in autoimmune arthritis. Nat Med 2014;20:62–8. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert‐Roth A, Ramos‐Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E, et al. Effect of interleukin‐6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 2008;371:987–97. - PubMed
-
- Genovese MC, McKay JD, Nasonov EL, Mysler EF, da Silva NA, Alecock E, et al. Interleukin‐6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs: the Tocilizumab in Combination With Traditional Disease‐Modifying Antirheumatic Drug Therapy study. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:2968–80. - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, Cantagrel A, van Vollenhoven R, Sanchez A, et al. IL‐6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti‐tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24‐week multicentre randomised placebo‐controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:1516–23. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kremer JM, Blanco R, Brzosko M, Burgos‐Vargas R, Halland AM, Vernon E, et al. Tocilizumab inhibits structural joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate responses to methotrexate: results from the double‐blind treatment phase of a randomized placebo‐controlled trial of tocilizumab safety and prevention of structural joint damage at one year. Arthritis Rheum 2011;63:609–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

