Ubiquitylation, neddylation and the DNA damage response
- PMID: 25833379
- PMCID: PMC4422126
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.150018
Ubiquitylation, neddylation and the DNA damage response
Abstract
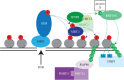
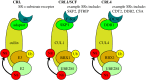
Failure of accurate DNA damage sensing and repair mechanisms manifests as a variety of human diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, immunodeficiency, infertility and cancer. The accuracy and efficiency of DNA damage detection and repair, collectively termed the DNA damage response (DDR), requires the recruitment and subsequent post-translational modification (PTM) of a complex network of proteins. Ubiquitin and the ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) SUMO have established roles in regulating the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). A role for other UBLs, such as NEDD8, is also now emerging. This article provides an overview of the DDR, discusses our current understanding of the process and function of PTM by ubiquitin and NEDD8, and reviews the literature surrounding the role of ubiquitylation and neddylation in DNA repair processes, focusing particularly on DNA DSB repair.
Keywords: DNA damage response; MLN4924; NEDD8; double-strand break repair; ubiquitin.
Figures


References
-
- Jackson SP, Bartek J. 2009. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 461, 1071–1078 (doi:10.1038/nature08467) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ciccia A, Elledge SJ. 2010. The DNA damage response: making it safe to play with knives. Mol. Cell 40, 179–204 (doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.019) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Polo SE, Jackson SP. 2011. Dynamics of DNA damage response proteins at DNA breaks: a focus on protein modifications. Genes Dev. 25, 409–433 (doi:10.1101/gad.2021311) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lindahl T. 1993. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature 22, 709–715 (doi:10.1038/362709a0) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bassing CH, Alt FW. 2004. The cellular response to general and programmed DNA double strand breaks. DNA Repair 3, 781–796 (doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.06.001) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
