Paravaginal aggressive angiomyxoma
- PMID: 25833906
- PMCID: PMC4401921
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-207287
Paravaginal aggressive angiomyxoma
Abstract
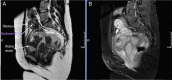
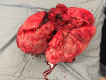
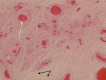
A 34-year-old nulliparous woman with a long-standing history of uterine fibroids and infertility had undergone prior open myomectomy, then uterine artery embolisation in treatment of an apparent large fibroid. Imaging on referral revealed an atypical 12×11×10 cm pelvic mass with the appearance of a fibroid. At laparotomy, the lesion was encapsulated but softer than a fibroid and located deep in the paravaginal space. The histopathological outcome was an aggressive angiomyxoma.
2015 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
