Antiviral therapies and prospects for a cure of chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 25833942
- PMCID: PMC4382723
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021501
Antiviral therapies and prospects for a cure of chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
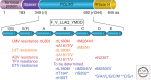
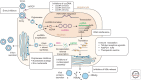
Current therapies of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) remain limited to either pegylated interferon-α (Peg-IFN-α), or one of the five approved nucleoside analog (NA) treatments. Although viral suppression can be achieved in the majority of patients with high-barrier-to-resistance new-generation NAs (i.e., entecavir and tenofovir), HBsAg loss is achieved in only 10% of patients with both classes of drugs after a follow-up of 5 years. Attempts to improve the response by administering two different NAs or a combination of NA and Peg-IFN-α have been unsuccessful. Therefore, there is a renewed interest to investigate a number of steps in the hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication cycle and specific virus-host cell interactions as potential targets for new antivirals. Novel targets and compounds could readily be evaluated using both relevant in vitro and newly developed in vivo models of HBV infection. The addition of one or several new drugs to current regimens should offer the prospect of markedly improving the response to therapy, thus reducing the burden of drug resistance, as well as the incidence of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Copyright © 2015 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Angers S, Li T, Yi X, MacCoss MJ, Moon RT, Zheng N 2006. Molecular architecture and assembly of the DDB1-CUL4A ubiquitin ligase machinery. Nature 443: 590–593. - PubMed
-
- Belloni L, Allweiss L, Guerrieri F, Pediconi N, Volz T, Pollicino T, Petersen J, Raimondo G, Dandri M, Levrero M 2012. IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J Clin Invest 122: 529–537. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belloni L, Li LC, Palumbo GA, Chirapu SR, Calvo L, Finn M, Lopatin U, Zlotnick A, Levrero M 2013. HAPs hepatitis B virus (HBV) capsid inhibitors block core protein interaction with the viral minichromosome and host cell genes and affect cccDNA transcription and stability. Hepatology 58: 277A.
-
- Berg T, Zoulim F, Moeller B, Trinh H, Marcellin P, Chan S, Kitrinos KM, Dinh P, Flaherty JF Jr, McHutchison JG, et al. 2014. Long-term efficacy and safety of emtricitabine plus tenofovir DF vs. tenofovir DF monotherapy in adefovir-experienced chronic hepatitis B patients. J Hepatol 60: 715–722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
