Fatal autoimmunity in mice reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells encoding defective FOXP3
- PMID: 25833964
- PMCID: PMC4473116
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-12-618363
Fatal autoimmunity in mice reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells encoding defective FOXP3
Abstract
Mice reconstituted with a human immune system provide a tractable in vivo model to assess human immune cell function. To date, reconstitution of murine strains with human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from patients with monogenic immune disorders have not been reported. One obstacle precluding the development of immune-disease specific "humanized" mice is that optimal adaptive immune responses in current strains have required implantation of autologous human thymic tissue. To address this issue, we developed a mouse strain that lacks murine major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC II) and instead expresses human leukocyte antigen DR1 (HLA-DR1). These mice displayed improved adaptive immune responses when reconstituted with human HSCs including enhanced T-cell reconstitution, delayed-type hypersensitivity responses, and class-switch recombination. Following immune reconstitution of this novel strain with HSCs from a patient with immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome, associated with aberrant FOXP3 function, mice developed a lethal inflammatory disorder with multiorgan involvement and autoantibody production mimicking the pathology seen in affected humans. This humanized mouse model permits in vivo evaluation of immune responses associated with genetically altered HSCs, including primary immunodeficiencies, and should facilitate the study of human immune pathobiology and the development of targeted therapeutics.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
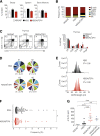



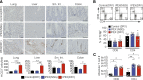

Comment in
-
Daring to learn from humanized mice.Blood. 2015 Jun 18;125(25):3829-31. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-04-639435. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26089378 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Stable hematopoietic cell engraftment after low-intensity nonmyeloablative conditioning in patients with immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Nov;126(5):1000-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.05.021. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20643476 Free PMC article.
-
Lentiviral Gene Therapy in HSCs Restores Lineage-Specific Foxp3 Expression and Suppresses Autoimmunity in a Mouse Model of IPEX Syndrome.Cell Stem Cell. 2019 Feb 7;24(2):309-317.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.12.003. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Cell Stem Cell. 2019. PMID: 30639036
-
Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) and IPEX-related disorders: an evolving web of heritable autoimmune diseases.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2013 Dec;25(6):708-14. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000029. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 24240290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of human forkhead box P3 in early thymic maturation and peripheral T-cell homeostasis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Dec;142(6):1909-1921.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.03.015. Epub 2018 Apr 27. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29705245
-
From IPEX syndrome to FOXP3 mutation: a lesson on immune dysregulation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018 Apr;1417(1):5-22. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13011. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018. PMID: 26918796 Review.
Cited by
-
Human CD4+CD8α+ Tregs induced by Faecalibacterium prausnitzii protect against intestinal inflammation.JCI Insight. 2022 Jun 22;7(12):e154722. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.154722. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35536673 Free PMC article.
-
Humanizing the mouse immune system to study splanchnic organ inflammation.J Physiol. 2018 Sep;596(17):3915-3927. doi: 10.1113/JP275325. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29574759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Status, Barriers, and Future Directions for Humanized Mouse Models to Evaluate Stem Cell-Based Islet Cell Transplant.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1387:89-106. doi: 10.1007/5584_2022_711. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35362861
-
The Sunrise of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures in Cancer.Immunol Rev. 2025 Jul;332(1):e70046. doi: 10.1111/imr.70046. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40591148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Humanized Mouse Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis for Studies on Immunopathogenesis and Preclinical Testing of Cell-Based Therapies.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 19;10:203. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00203. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30837986 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Suntharalingam G, Perry MR, Ward S, et al. Cytokine storm in a phase 1 trial of the anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody TGN1412. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(10):1018–1028. - PubMed
-
- McKenzie R, Fried MW, Sallie R, et al. Hepatic failure and lactic acidosis due to fialuridine (FIAU), an investigational nucleoside analogue for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(17):1099–1105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 AI050950/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK097894/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050950/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI075037/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI075037/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI075037/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- TGT11A04/TI_/Telethon/Italy
- F32DK097894/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI50950/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059561/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

