GluA2 trafficking is involved in apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells induced by activation of EphB/EphrinB reverse signaling in a rat chronic ocular hypertension model
- PMID: 25834064
- PMCID: PMC6705403
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4376-14.2015
GluA2 trafficking is involved in apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells induced by activation of EphB/EphrinB reverse signaling in a rat chronic ocular hypertension model
Abstract
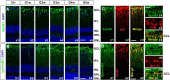
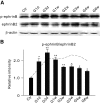
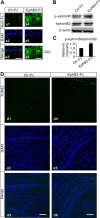
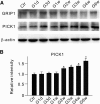
EphB1, expressed in Müller cells, and ephrinB2, expressed in both Müller cells and retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), constitute an EphB/ephrinB reverse signaling in RGCs. Whether and how this reverse signaling is involved in RGC apoptosis in a rat chronic ocular hypertension (COH) model was investigated. In the COH model, both EphB1 and ephrinB2 were significantly increased and the reverse signaling was activated, which was accompanied by increased protein levels of phosphorylated (p) src, GluA2, and p-GluA2. Intravitreal injection of EphB2-Fc, an activator of ephrinB2, induced an increase in TUNEL-positive signals in normal retinae. A coimmunoprecipitation assay demonstrated direct interactions among ephrinB2, p-src, and GluA2. Moreover, in COH rats the expression of GluA2 proteins on the surface of retinal cells was decreased. Such GluA2 endocytosis could be prevented by preoperational intravitreal injection of 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazolo [3,4-d] pyrimidine (PP2), an inhibitor of src family tyrosine kinases, and possibly involved the protein interacting with C kinase 1 and phosphorylation of GluA2. In normal rats, intravitreal injection of EphB2-Fc caused changes in these protein levels similar to those observed in COH rats, which all could be avoided by preinjection of PP2. Patch-clamp experiments further showed that the current-voltage relationship of AMPA receptor-mediated EPSCs of RGCs exhibited stronger inward rectification in EphB2-Fc-injected rats. Furthermore, preinjection of PP2 or N-[3-[[4-[(3-aminopropyl)amino]butyl]amino]propyl]-1-naphthaleneacetamide trihydrochloride) (Naspm), a Ca(2+)-permeable GluA2-lacking AMPA receptor inhibitor, remarkably inhibited RGC apoptosis in either EphB2-Fc-injected or COH rats. Together, elevated GluA2 trafficking induced by activated EphB2/ephrinB2 reverse signaling likely contributes to RGC apoptosis in COH rats.
Keywords: AMPA receptor trafficking; EphB/ephrinB reverse signaling; GluA2; apoptosis; glaucoma; retinal ganglion cell.
Copyright © 2015 the authors 0270-6474/15/355409-13$15.00/0.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Involvement of mGluR I in EphB/ephrinB reverse signaling activation induced retinal ganglion cell apoptosis in a rat chronic hypertension model.Brain Res. 2018 Mar 15;1683:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.01.017. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29366625
-
EphrinB/EphB forward signaling in Müller cells causes apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells by increasing tumor necrosis factor alpha production in rat experimental glaucomatous model.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018 Oct 24;6(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s40478-018-0618-x. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018. PMID: 30355282 Free PMC article.
-
Activated ephrinA3/EphA4 forward signaling induces retinal ganglion cell apoptosis in experimental glaucoma.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Nov 1;178:108228. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108228. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32745487
-
Calcium channels are involved in EphB/ephrinB reverse signaling‑induced apoptosis in a rat chronic ocular hypertension model.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Feb;17(2):2465-2471. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8162. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29207174 Free PMC article.
-
[Glutamate receptor-mediated retinal neuronal injury in experimental glaucoma].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2016 Aug 25;68(4):483-91. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27546508 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
L- and T-type Ca2+ channels dichotomously contribute to retinal ganglion cell injury in experimental glaucoma.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Jul;18(7):1570-1577. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.360277. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36571364 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Müller cells and microglia aggravates retinal inflammatory response in experimental glaucoma.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Dec 24;18(1):303. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02366-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34952606 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles reduce glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in the retina.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Oct;18(10):2315-2320. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.369123. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 37056153 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Characterization and Interspecies Evolution of the Tree Shrew Retina across Postnatal Lifespan.Research (Wash D C). 2024 Nov 21;7:0536. doi: 10.34133/research.0536. eCollection 2024. Research (Wash D C). 2024. PMID: 39574940 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular Hypertension Drives Remodeling of AMPA Receptors in Select Populations of Retinal Ganglion Cells.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020 Jul 24;12:30. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2020.00030. eCollection 2020. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32792936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calò L, Bruno V, Spinsanti P, Molinari G, Korkhov V, Esposito Z, Patanè M, Melchiorri D, Freissmuth M, Nicoletti F. Interactions between ephrin-B and metabotropic glutamate 1 receptors in brain tissue and cultured neurons. J Neurosci. 2005a;25:2245–2254. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4956-04.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
