Memories that last in hypertension
- PMID: 25834073
- PMCID: PMC4451327
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00633.2014
Memories that last in hypertension
Abstract
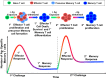
In recent years, it has become clear that the immune system contributes to the genesis of hypertension. Hypertensive stimuli, such as angiotensin II, DOCA-salt, and norepinephrine, cause T cells and monocytes/macrophages to accumulate in the kidney and vasculature. These cells release inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, interferon-γ, and IL-17, that promote renal and vascular dysfunction. These cytokines also promote angiotensinogen production in the proximal tubule and Na(+) retention in the distal nephron and contribute to renal fibrosis and glomerular damage. For several years, we have observed accumulation of memory T cells in the kidney and vasculature. Given the propensity for memory cells to produce cytokines such as interferon-γ and IL-17, interventions to prevent the formation or renal accumulation of specific memory T cell subsets could prevent end-organ damage and blood pressure elevation in response to hypertensive stimuli.
Keywords: CD70; T cells; adaptive immunity; cytokines; immunological memory.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Bevan MJ. Helping the CD8+ T-cell response. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 595–602, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Dickinson CJ, Lawrence JR. A slowly developing pressor response to small concentrations of angiotensin. Its bearing on the pathogenesis of chronic renal hypertension. Lancet 1: 1354–1356, 1963. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Villalobos RA, Janjoulia T, Fletcher NK, Giani JF, Nguyen MT, Riquier-Brison AD, Seth DM, Fuchs S, Eladari D, Picard N, Bachmann S, Delpire E, Peti-Peterdi J, Navar LG, Bernstein KE, McDonough AA. The absence of intrarenal ACE protects against hypertension. J Clin Invest 123: 2011–2023, 2013. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01-GM-015431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1-F32-HL-124972-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL039006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL-095070/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL058000/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL124972/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125865/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-108701/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL-058000/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-039006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-105294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

