The investigational Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) induces cell cycle G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38 MAPK and Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 25834401
- PMCID: PMC4365748
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S75378
The investigational Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) induces cell cycle G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38 MAPK and Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in human breast cancer cells
Abstract
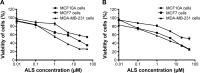
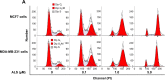
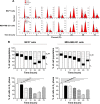
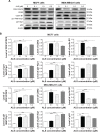
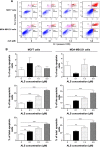
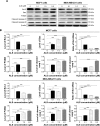
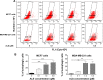
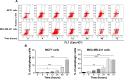
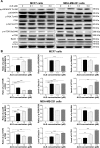
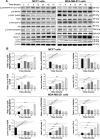
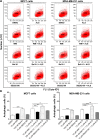
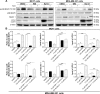
Alisertib (ALS) is an investigational potent Aurora A kinase inhibitor currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of hematological and non-hematological malignancies. However, its antitumor activity has not been tested in human breast cancer. This study aimed to investigate the effect of ALS on the growth, apoptosis, and autophagy, and the underlying mechanisms in human breast cancer MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. In the current study, we identified that ALS had potent growth-inhibitory, pro-apoptotic, and pro-autophagic effects in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. ALS arrested the cells in G2/M phase in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells which was accompanied by the downregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)1/cell division cycle (CDC) 2, CDK2, and cyclin B1 and upregulation of p21 Waf1/Cip1, p27 Kip1, and p53, suggesting that ALS induces G2/M arrest through modulation of p53/p21/CDC2/cyclin B1 pathways. ALS induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells; ALS significantly decreased the expression of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), but increased the expression of B-cell lymphoma 2-associated X protein (Bax) and p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA), and increased the expression of cleaved caspases 3 and 9. ALS significantly increased the expression level of membrane-bound microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3)-II and beclin 1 and induced inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells as indicated by their altered phosphorylation, contributing to the pro-autophagic activities of ALS. Furthermore, treatment with wortmannin markedly downregulated ALS-induced p38 MAPK activation and LC3 conversion. In addition, knockdown of the p38 MAPK gene by ribonucleic acid interference upregulated Akt activation and resulted in LC3-II accumulation. These findings indicate that ALS promotes cellular apoptosis and autophagy in breast cancer cells via modulation of p38 MAPK/Akt/mTOR pathways. Further studies are warranted to further explore the molecular targets of ALS in the treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: ALS; apoptosis; autophagy; breast cancer; cell cycle; p38 MAPK.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pro-apoptotic and pro-autophagic effects of the Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) on human osteosarcoma U-2 OS and MG-63 cells through the activation of mitochondria-mediated pathway and inhibition of p38 MAPK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Mar 12;9:1555-84. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S74197. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25792811 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of mitotic Aurora kinase A by alisertib induces apoptosis and autophagy of human gastric cancer AGS and NCI-N78 cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jan 14;9:487-508. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S74127. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25609923 Free PMC article.
-
The pan-inhibitor of Aurora kinases danusertib induces apoptosis and autophagy and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Feb 17;9:1027-62. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S74412. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25733818 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR Intracellular Pathway and Breast Cancer: Factors, Mechanism and Regulation.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(11):1633-1638. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666161116125218. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 27848885 Review.
-
Emerging roles of the p38 MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways in oncogene-induced senescence.Trends Biochem Sci. 2014 Jun;39(6):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 May 9. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014. PMID: 24818748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alisertib and Barasertib Induce Cell Cycle Arrest and Mitochondria-Related Cell Death in Multiple Myeloma with Enhanced Efficacy Through Sequential Combination with BH3-Mimetics and Panobinostat.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 9;17(14):2290. doi: 10.3390/cancers17142290. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723174 Free PMC article.
-
The Aurora kinase A inhibitor TC-A2317 disrupts mitotic progression and inhibits cancer cell proliferation.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):84718-84735. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12448. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713168 Free PMC article.
-
Ursolic Acid Exhibits Potent Anticancer Effects in Human Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Cells (SK-MEL-24) via Apoptosis Induction, Inhibition of Cell Migration and Invasion, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Inhibition of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK)/ERK Signaling Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Feb 17;25:1283-1290. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913069. Med Sci Monit. 2019. Retraction in: Med Sci Monit. 2021 Jan 16;27:e930758. doi: 10.12659/MSM.930758. PMID: 30772887 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
DNA hypermethylation of aurora kinase A in hepatitis C virus‑positive hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Sep;20(3):2519-2532. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10487. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31322223 Free PMC article.
-
New Advances in Targeted Therapy of HER2-Negative Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 4;12:828438. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.828438. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35311116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):52–62. - PubMed
-
- Kasami M, Uematsu T, Honda M, et al. Sugimura, Comparison of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and Her-2 status in breast cancer pre-and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast. 2008;17(5):523–527. - PubMed
-
- Morgan G, Ward R, Barton M. The contribution of cytotoxic chemotherapy to 5-year survival in adult malignancies. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2004;16(8):549–560. - PubMed
-
- Okada H, Mak TW. Pathways of apoptotic and non-apoptotic death in tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(8):592–603. - PubMed
-
- Fu J, Bian M, Jiang Q, Zhang C. Roles of Aurora kinases in mitosis and tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5(1):1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

