Rosa damascena oil improves SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction in male patients suffering from major depressive disorders: results from a double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 25834441
- PMCID: PMC4358691
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S78696
Rosa damascena oil improves SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction in male patients suffering from major depressive disorders: results from a double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: A substantial disadvantage of psychopharmacological treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) with selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) is the impact on sexual dysfunction. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether the oil of Rosa damascena can have a positive influence on SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction (SSRI-I SD) of male patients who are suffering from MDD and are being treated with SSRIs.
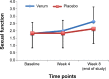
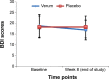
Method: In a double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled clinical trial, a total of 60 male patients treated with an SSRI and suffering from MDD (mean age =32 years) and SSRI-I SD were randomly assigned to take either verum (R. damascena oil) or a placebo. Patients completed self-ratings of depression and sexual function at baseline, at 4 weeks later, and at the end of the study, 8 weeks after it started.
Results: Over time, sexual dysfunction improved more in the verum group than in the control group. Improvements were observed in the verum group from week 4 to week 8. Self-rated symptoms of depression reduced over time in both groups, but did so more so in the verum group than in the control group.
Conclusion: This double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled clinical trial showed that the administration of R. damascena oil ameliorates sexual dysfunction in male patients suffering from both MDD and SSRI-I SD. Further, the symptoms of depression reduced as sexual dysfunction improved.
Keywords: Rosa damascena oil; SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction; major depressive disorder; selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors; sexual dysfunction.
Figures
References
-
- Josefsson T, Lindwall M, Archer T. Physical exercise intervention in depressive disorders: meta-analysis and systematic review. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014;24(2):259–272. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Global mortality, disability, and the contribution of risk factors: global burden of disease study. Lancet. 1997;349(9063):1436–1442. - PubMed
-
- Johannes CB, Clayton AH, Odom DM, et al. Distressing sexual problems in United States women revisited: prevalence after accounting for depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70(12):1698–1706. - PubMed
-
- Bonierbale M, Lançon C, Tignol J. The ELIXIR study: evaluation of sexual dysfunction in 4557 depressed patients in France. Curr Medl Res Opin. 2003;19(2):114–124. - PubMed
-
- Angst J. Sexual problems in healthy and depressed persons. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1998;13(Suppl 6):S1–S4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

