Depth determination of skin cancers treated with superficial brachytherapy: ultrasound vs. histopathology
- PMID: 25834579
- PMCID: PMC4300362
- DOI: 10.5114/jcb.2014.47860
Depth determination of skin cancers treated with superficial brachytherapy: ultrasound vs. histopathology
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to compare high frequency ultrasonography (HFUS) and histpathologic assessment done by punch biopsy in order to determine depth of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), in both superficial and nodular BCCs prior to brachytherapy treatment.
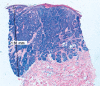
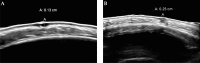
Material and methods: This study includes 20 patients with 10 superficial and 10 nodular BCCs. First, punch biopsy was done to confirm the diagnosis and to measure tumour depth (Breslow rate). Subsequently, HFUS was done to measure tumour depth to search for correlation of these two techniques.
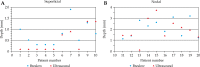
Results: Neither clear tendency nor significance of the punch biopsy vs. HFUS depth determination is observed. Depth value differences with both modalities resulted patient dependent and then consequence of its uncertainty. Conceptually, HFUS should determine the macroscopic lesion (gross tumour volume - GTV), while punch biopsy is able to detect the microscopic extension (clinical target volume - CTV). Uncertainties of HFUS are difficult to address, while punch biopsy is done just on a small lesion section, not necessarily the deepest one.
Conclusions: According to the results, HFUS is less accurate at very shallow depths. Nodular cases present higher depth determination differences than superficial ones. In our clinical practice, we decided to prescribe at 3 mm depth when HFUS measurements give depth lesion values smaller than this value.
Keywords: basal cell carcinoma; electronic brachytherapy; punch biopsy; skin brachytherapy; skin cancer; ultrasound.
Figures
References
-
- Lear W, Dahlke E, Murray CA. Basal cell carcinoma: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and associated risk factors. J Cutan Med Surg. 2007;11:19–30. - PubMed
-
- Fimhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:161–168. - PubMed
-
- Roozeboom MH, Arits AH, Nelemans PJ, et al. Overall treatment success after treatment of primary superficial basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and nonrandomized trials. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:733–756. - PubMed
-
- Bahner JD, Bordeaux JS. Non-melanoma skin cancers: photodynamic therapy, cryotherapy, 5-fluorouracil, imiquimod, diclofenac, or what? Facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:792–798. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
