Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate monotherapy for nucleos(t)ide analogue-naïve and nucleos(t)ide analogue-experienced chronic hepatitis B patients
- PMID: 25834801
- PMCID: PMC4379196
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2015.21.1.41
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate monotherapy for nucleos(t)ide analogue-naïve and nucleos(t)ide analogue-experienced chronic hepatitis B patients
Abstract
Background/aims: This study investigated the antiviral effects of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) monotherapy in nucleos(t)ide analogue (NA)-naive and NA-experienced chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients.
Methods: CHB patients treated with TDF monotherapy (300 mg/day) for ≥12 weeks between December 2012 and July 2014 at a single center were retrospectively enrolled. Clinical, biochemical, and virological parameters were assessed every 12 weeks.
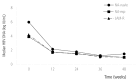
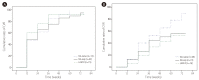
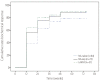
Results: In total, 136 patients (median age 49 years, 96 males, 94 HBeAg positive, and 51 with liver cirrhosis) were included. Sixty-two patients were nucleos(t)ide (NA)-naïve, and 74 patients had prior NA therapy (NA-exp group), and 31 patients in the NA-exp group had lamivudine (LAM)-resistance (LAM-R group). The baseline serum hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA level was 4.9±2.3 log IU/mL (mean±SD), and was higher in the NA-naïve group than in the NA-exp and LAM-R groups (5.9±2.0 log IU/mL vs 3.9±2.0 log IU/mL vs 4.2±1.7 log IU/mL, P<0.01). The complete virological response (CVR) rate at week 48 in the NA-naïve group (71.4%) did not differ significantly from those in the NA-exp (71.3%) and LAM-R (66.1%) groups. In multivariate analysis, baseline serum HBV DNA was the only predictive factor for a CVR at week 48 (hazard ratio, 0.809; 95% confidence interval, 0.729-0.898), while the CVR rate did not differ with the NA experience.
Conclusions: TDF monotherapy was effective for CHB treatment irrespective of prior NA treatment or LAM resistance. Baseline serum HBV DNA was the independent predictive factor for a CVR.
Keywords: Chronic Hepatitis B; Lamivudine-resistant; Nucleos(t)ide analogue-experienced; Tenofovir.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Liaw YF, Chu CM. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2009;373:582–592. - PubMed
-
- Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006;295:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Chen CJ. Predicting cirrhosis risk based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:678–686. - PubMed
-
- Mommeja-Marin H, Mondou E, Blum MR, Rousseau F. Serum HBV DNA as a marker of efficacy during therapy for chronic HBV infection: analysis and review of the literature. Hepatology. 2003;37:1309–1319. - PubMed
-
- Liaw YF. Impact of therapy on the long-term outcome of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Liver Dis. 2013;17:413–423. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

