Autism spectrum disorders and intestinal microbiota
- PMID: 25835343
- PMCID: PMC4616908
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2015.1035855
Autism spectrum disorders and intestinal microbiota
Abstract
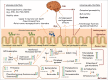
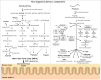
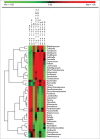
Through extensive microbial-mammalian co-metabolism, the intestinal microbiota have evolved to exert a marked influence on health and disease via gut-brain-microbiota interactions. In this addendum, we summarize the findings of our recent study on the fecal microbiota and metabolomes of children with pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS) or autism (AD) compared with healthy children (HC). Children with PDD-NOS or AD have altered fecal microbiota and metabolomes (including neurotransmitter molecules). We hypothesize that the degree of microbial alteration correlates with the severity of the disease since fecal microbiota and metabolomes alterations were higher in children with PDD-NOS and, especially, AD compared to HC. Our study indicates that the levels of free amino acids (FAA) and volatile organic compounds (VOC) differ in AD subjects compared to children with PDD-NOS, who are more similar to HC. Finally, we propose a new perspective on the implications for the interaction between intestinal microbiota and AD.
Keywords: ASD; dysbiosis; intestinal microbiota; metabolome; perspective.
Figures
References
-
- Petrof EO, Claud EC, Gloor GB, Allen-Vercoe E. Microbial ecosystems therapeutics: a new paradigm in medicine? Benef Microbes 2013; 4:53-65; PMID:23257018; http//dx.doi.org/ 10.3920/BM2012.0039 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sekirov I, Russell SL, Antunes LCM, Finlay BB. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol Rev 2010; 90:859-904; PMID:20664075; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1152/physrev.00045.2009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stilling RM, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Microbial genes, brain & behaviour – epigenetic regulation of the gut–brain axis. Genes, Brain and Behavior 2014; 13:69-86; PMID:24286462; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/gbb.12109 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Kasper LH. The role of microbiome in central nervous system disorders. Brain Behav. Immunology 2013; pii: S0889-1591(13)00600-4; PMID:24370461; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.bbi.2013.12.015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bravo JA, Forsythe P, Chew MV, Escaravage E, Savignac HM, Dinan TG, Bienenstock J, Cryan JF. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behaviour and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011; 108:16050-55; PMID:21876150; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1073/pnas.1102999108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
