Albumin induces excitatory synaptogenesis through astrocytic TGF-β/ALK5 signaling in a model of acquired epilepsy following blood-brain barrier dysfunction
- PMID: 25836421
- PMCID: PMC4426044
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.02.029
Albumin induces excitatory synaptogenesis through astrocytic TGF-β/ALK5 signaling in a model of acquired epilepsy following blood-brain barrier dysfunction
Abstract
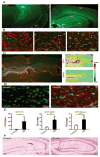
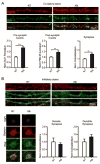
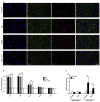
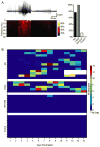
Post-injury epilepsy (PIE) is a common complication following brain insults, including ischemic, and traumatic brain injuries. At present, there are no means to identify the patients at risk to develop PIE or to prevent its development. Seizures can occur months or years after the insult, do not respond to anti-seizure medications in over third of the patients, and are often associated with significant neuropsychiatric morbidities. We have previously established the critical role of blood-brain barrier dysfunction in PIE, demonstrating that exposure of brain tissue to extravasated serum albumin induces activation of inflammatory transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling in astrocytes and eventually seizures. However, the link between the acute astrocytic inflammatory responses and reorganization of neural networks that underlie recurrent spontaneous seizures remains unknown. Here we demonstrate in vitro and in vivo that activation of the astrocytic ALK5/TGF-β-pathway induces excitatory, but not inhibitory, synaptogenesis that precedes the appearance of seizures. Moreover, we show that treatment with SJN2511, a specific ALK5/TGF-β inhibitor, prevents synaptogenesis and epilepsy. Our findings point to astrocyte-mediated synaptogenesis as a key epileptogenic process and highlight the manipulation of the TGF-β-pathway as a potential strategy for the prevention of PIE.
Keywords: ALK5; Albumin; Astrocytes; Blood–brain barrier (BBB); Epilepsy; Post-insult epilepsy (PIE); Post-traumatic epilepsy (PTE); Seizures; Synaptogenesis; TGF-β.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Babb TL, Kupfer WR, Pretorius JK, Crandall PH, Levesque MF. Synaptic reorganization by mossy fibers in human epileptic fascia dentata. Neuroscience. 1991;42:351–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

