Propofol ameliorates calpain-induced collapsin response mediator protein-2 proteolysis in traumatic brain injury in rats
- PMID: 25836613
- PMCID: PMC4834009
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.154298
Propofol ameliorates calpain-induced collapsin response mediator protein-2 proteolysis in traumatic brain injury in rats
Abstract
Background: Collapsin response mediator protein-2 (CRMP2), a multifunctional cytosolic protein highly expressed in the brain, is degraded by calpain following traumatic brain injury (TBI), possibly inhibiting posttraumatic neurite regeneration. Lipid peroxidation (LP) is involved in triggering postinjury CRMP2 proteolysis. We examined the hypothesis that propofol could attenuate LP, calpain-induced CRMP2 degradation, and brain injury after TBI.
Methods: A unilateral moderate controlled cortical impact injury was induced in adult male Sprague-Dawley rats. The animals were randomly divided into seven groups: Sham control group, TBI group, TBI + propofol groups (including propofol 1 h, 2 h, and 4 h groups), TBI + U83836E group and TBI + fat emulsion group. The LP inhibitor U83836E was used as a control to identify that antioxidation partially accounts for the potential neuroprotective effects of propofol. The solvent of propofol, fat emulsion, was used as the vehicle control. Ipsilateral cortex tissues were harvested at 24 h post-TBI. Immunofluorescent staining, Western blot analysis, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling were used to evaluate LP, calpain activity, CRMP2 proteolysis and programmed cell death. The data were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and a paired t-test.
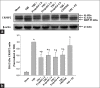
Results: Propofol and U83836E significantly ameliorated the CRMP2 proteolysis. In addition, both propofol and U83836E significantly decreased the ratio of 145-kDa αII-spectrin breakdown products to intact 270-kDa spectrin, the 4-hydroxynonenal expression and programmed cell death in the pericontusional cortex at 24 h after TBI. There was no difference between the TBI group and the fat emulsion group.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that propofol postconditioning alleviates calpain-mediated CRMP2 proteolysis and provides neuroprotective effects following moderate TBI potentially by counteracting LP and reducing calpain activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Georgiou AP, Manara AR. Role of therapeutic hypothermia in improving outcome after traumatic brain injury: A systematic review. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110:357–67. - PubMed
-
- Luo T, Wu J, Kabadi SV, Sabirzhanov B, Guanciale K, Hanscom M, et al. Propofol limits microglial activation after experimental brain trauma through inhibition of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase. Anesthesiology. 2013;119:1370–88. - PubMed
-
- Boer C, Franschman G, Loer SA. Prehospital management of severe traumatic brain injury: Concepts and ongoing controversies. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2012;25:556–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

