Interstitial lung disease in scleroderma
- PMID: 25836640
- PMCID: PMC4385198
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rdc.2014.12.005
Interstitial lung disease in scleroderma
Abstract
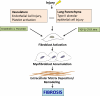
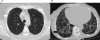
Systemic sclerosis is a heterogeneous disease of unknown etiology with limited effective therapies. It is characterized by autoimmunity, vasculopathy, and fibrosis and is clinically manifested by multiorgan involvement. Interstitial lung disease is a common complication of systemic sclerosis and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The diagnosis of interstitial lung disease hinges on careful clinical evaluation and pulmonary function tests and high-resolution computed tomography. Effective therapeutic options are still limited. Several experimental therapies are currently in early-phase clinical trials and show promise.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Fibrosis; Interstitial lung disease; Pathogenesis; Systemic sclerosis; Treatment.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Schurawitzki H, Stiglbauer R, Graninger W, et al. Interstitial lung disease in progressive systemic sclerosis: high-resolution CT versus radiography. Radiology. 1990;176(3):755–9. - PubMed
-
- Steen VD, Owens GR, Fino GJ, et al. Pulmonary involvement in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 1985;28(7):759–67. - PubMed
-
- Steen VD, Conte C, Owens GR, et al. Severe restrictive lung disease in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37(9):1283–9. - PubMed
-
- McNearney TA, Reveille JD, Fischbach M, et al. Pulmonary involvement in systemic sclerosis: associations with genetic, serologic, sociodemographic, and behavioral factors. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57(2):318–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

