Deep Sclerectomy With a New Nonabsorbable Uveoscleral Implant (Esnoper-Clip): 1-Year Outcomes
- PMID: 25836660
- PMCID: PMC4521906
- DOI: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000000253
Deep Sclerectomy With a New Nonabsorbable Uveoscleral Implant (Esnoper-Clip): 1-Year Outcomes
Abstract
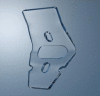
Purpose: To report the safety and the effectiveness of deep sclerectomy (DS) with a new nonabsorbable uveoscleral hema implant (Esnoper-Clip) designed to increase trabecular and uveoscleral outflow and to achieve higher intrascleral blebs.
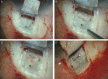
Materials and methods: Twenty-seven eyes of 27 patients with open-angle glaucoma, who underwent DS with an Esnoper-Clip implant, were included in this study. All patients were followed up after 12 months.
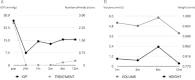
Results: A significant decrease in intraocular pressure was observed after surgery, changing from a preoperative mean of 26.6±5.2 mm Hg to a postoperative mean of 15.3±5 mm Hg (P<0.001) at 12 months. There was also a significant reduction in the number of glaucoma drugs needed, varying from 2.5 per patient to 0.3 (P<0.001) 1 year after surgery. The main intrascleral lake height and volume at 12 months was 0.7±0.1 mm and 3.9±1.3 mm, respectively. No intraoperative complications occurred. The main postoperative complications were a positive Seidel test result at 24 hours in 2 eyes (7.4%), hyphema in 2 eyes (7.4%), and choroidal detachment in 1 eye (3.7%). All these complications resolved successfully. The need for additional mitomycin-C injections was recorded in 4 eyes (14.8%), twice in 2 of them. Twelve eyes (44.4%) underwent postsurgical Nd:YAG laser goniopuncture with a mean time between surgery and this procedure of 4.3 months. Mean intraocular pressure after Nd:YAG laser goniopuncture decreased from 19.2 to 15.5 mm Hg (P<0.001).
Conclusion: DS with an uveoscleral hema implant (Esnoper-Clip) is a safe and effective technique for the management of open-angle glaucoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
References
-
- Muñoz G. Nonstitch suprachoroidal technique for T-flux® implantation in deep sclerectomy. J Glaucoma. . 2009;18:262–264. - PubMed
-
- Mavrakanas N, Mendrinos E, Shaarawy T. Postoperative IOP is related to intrascleral bleb height in eyes with clinically flat blebs following deep sclerectomy with collagen implant and mitomycin. Br J Ophthalmol. . 2010;94:410–413. - PubMed
-
- Pérez-Rico C, Gutiérrez-Ortíz C, Moreno-Salgueiro A, et al. Visante anterior segment optical coherence tomography analysis of morphologic changes after deep sclerectomy with intraoperative mitomycin-C and no implant use. J Glaucoma. . 2014;23:e86–e90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

