A practical guide to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of neonatal infections
- PMID: 25836710
- PMCID: PMC7127476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcl.2014.11.010
A practical guide to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of neonatal infections
Abstract
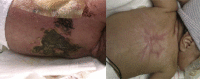
Neonatal infections continue to cause morbidity and mortality in infants. Among approximately 400,000 infants followed nationally, the incidence rates of early-onset sepsis infection within 3 days of life are 0.98 cases per 1000 live births. Newborn infants are at increased risk for infections because they have relative immunodeficiency. This article provides evidence-based practical approaches to the diagnosis, management, and prevention of neonatal infections.
Keywords: Antibacterial therapy; Antiviral therapy; Early-onset sepsis; Late-onset sepsis; Neonatal antimicrobial stewardship; Neonatal infections; Newborn sepsis; Respiratory viral infections in infants.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Schelonka R.L., Maheshwari A. The many faces of B cells: from generation of antibodies to immune regulation. NeoReviews. 2013;14:e438–e447.
-
- Levy O. Innate immunity of the newborn: basic mechanisms and clinical correlates. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(5):379–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical