Primary bladder lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell type: Case report and literature review of 26 cases
- PMID: 25837971
- PMCID: PMC4374275
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-7796.152947
Primary bladder lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell type: Case report and literature review of 26 cases
Abstract
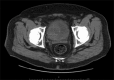
Primary lymphoma of the urinary bladder is exceedingly rare, representing 0.2% of all extranodal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Although Matsuno et al. and others state the most common type is mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma, 20% of all the primary lymphomas of the urinary bladder are considered to be high grade neoplasms; the majority being diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). This is a case report of a 48-year-old man that presented with hematuria, frequency, nocturia, and flank pain that was found to have high grade DLBCL. Twenty-six other cases of both low and high grade primary bladder lymphomas were selected in order to provide a thorough comparison of different treatment modalities. Of the cases reviewed, bladder lymphoma was more common in females (2:1). The average age at diagnosis was 63.9 years old (low grade: 68.7 years old, high grade: 58.8 years old). The most common low-grade neoplasm was MALT lymphoma (85.7%). For the low-grade malignancies, the most successful treatments were simple therapies (2 transurethral resection of a bladder tumour [TURBT], 1 antibiotics), solitary chemotherapy, and combination TURBT/chemo; all 3 of which achieved 100% clinical remission (CR) in the cases reviewed. The most common high grade neoplasm was DLBCL (76.9%). The most successful therapies used to treat high grade lesions were solitary chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, duanorubacin, vincristine, prednisolone [CHOP] or ritoximab, CHOP [R-CHOP]) and combination therapies (2 radiation/CHOP, 2 surgery/CHOP). In the agreement with the current literature, this review has shown that simple therapies (TURBT) are equally as effective as aggressive treatments (chemotherapy, radiation) and should therefore be used as first line treatment in low grade tumors. For high grade malignancies, chemotherapy (R-CHOP or CHOP) alone or combination therapy (CHOP/surgery or CHOP/radiation) is recommended.
Keywords: Cyclophosphamide; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; duanorubacin; extranodal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; hematuria; prednisolone chemotherapy; primary bladder lymphoma; vincristine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Mourad WA, Khalil S, Radwi A, Peracha A, Ezzat A. Primary T-cell lymphoma of the urinary bladder. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:373–7. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Cao ZZ, Qi L. Primary T-cell lymphoma of the urinary bladder presenting with haematuria and hydroureteronephrosis. J Int Med Res. 2011;39:2027–32. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs A, Symington T. Primary lymphosarcoma of urinary bladder. Br J Urol. 1953;25:119–26. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

