Myocardial Infarction-Associated SNP at 6p24 Interferes With MEF2 Binding and Associates With PHACTR1 Expression Levels in Human Coronary Arteries
- PMID: 25838425
- PMCID: PMC4441556
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305534
Myocardial Infarction-Associated SNP at 6p24 Interferes With MEF2 Binding and Associates With PHACTR1 Expression Levels in Human Coronary Arteries
Abstract
Objective: Coronary artery disease (CAD), including myocardial infarction (MI), is the main cause of death in the world. Genome-wide association studies have identified dozens of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with CAD/MI. One of the most robust CAD/MI genetic associations is with intronic SNPs in the gene PHACTR1 on chromosome 6p24. How these PHACTR1 SNPs influence CAD/MI risk, and whether PHACTR1 itself is the causal gene at the locus, is currently unknown.
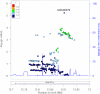
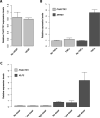
Approach and results: Using genetic fine-mapping and DNA resequencing experiments, we prioritized an intronic SNP (rs9349379) in PHACTR1 as causal variant. We showed that this variant is an expression quantitative trait locus for PHACTR1 expression in human coronary arteries. Experiments in endothelial cell extracts confirmed that alleles at rs9349379 are differentially bound by the transcription factors myocyte enhancer factor-2. We engineered a deletion of this myocyte enhancer factor-2-binding site using CRISPR/Cas9 genome-editing methodology. Heterozygous endothelial cells carrying this deletion express 35% less PHACTR1. Finally, we found no evidence that PHACTR1 expression levels are induced when stimulating human endothelial cells with vascular endothelial growth factor, tumor necrosis factor-α, or shear stress.
Conclusions: Our results establish a link between intronic SNPs in PHACTR1, myocyte enhancer factor-2 binding, and transcriptional functions at the locus, PHACTR1 expression levels in coronary arteries and CAD/MI risk. Because PHACTR1 SNPs are not associated with the traditional risk factors for CAD/MI (eg, blood lipids or pressure, diabetes mellitus), our results suggest that PHACTR1 may influence CAD/MI risk through as yet unknown mechanisms in the vascular endothelium.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; genetic association studies; myocardial infarction.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


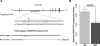
Comment in
-
PHACTR1: Functional Clues Linking a Genome-Wide Association Study Locus to Coronary Artery Disease.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Jun;35(6):1293-5. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305680. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25995042 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: Systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367:1747–1757. - PubMed
-
- Barter PJ, Caulfield M, Eriksson M, et al. Effects of torcetrapib in patients at high risk for coronary events. The New England journal of medicine. 2007;357:2109–2122. - PubMed
-
- Nissen SE, Tardif JC, Nicholls SJ, Revkin JH, Shear CL, Duggan WT, Ruzyllo W, Bachinsky WB, Lasala GP, Tuzcu EM. Effect of torcetrapib on the progression of coronary atherosclerosis. The New England journal of medicine. 2007;356:1304–1316. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz GG, Olsson AG, Abt M, et al. Effects of dalcetrapib in patients with a recent acute coronary syndrome. The New England journal of medicine. 2012;367:2089–2099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL088531/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CIHR-MOP136979/Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Canada
- RC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL-102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL107816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL-102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127564/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CIHR-MOP102489/Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Canada
- RC2 HL-102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM104464/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5U54HG003067-11/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL-102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM104464/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD057194/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL-103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

