Nonclassical patrolling monocyte function in the vasculature
- PMID: 25838429
- PMCID: PMC4441550
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304650
Nonclassical patrolling monocyte function in the vasculature
Abstract
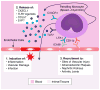
Nonclassical patrolling monocytes are characterized by their unique ability to actively patrol the vascular endothelium under homeostatic and inflammatory conditions. Patrolling monocyte subsets (CX3CR1(high)Ly6C(-) in mouse and CX3CR1(high)CD14(dim)CD16(+) in humans) are distinct from the classical monocyte subsets (CCR2(high)Ly6C(+) in mouse and CCR2(high)CD14(+)CD16(-) in humans) and exhibit unique functions in the vasculature and inflammatory disease. Patrolling monocytes function in several disease settings to remove damaged cells and debris from the vasculature and have been associated with wound healing and the resolution of inflammation in damaged tissues. This review highlights the unique functions of these patrolling monocytes in the vasculature and during inflammation.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; inflammation; macrophages; monocytes.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Swirski FK. Monocyte recruitment and macrophage proliferation in atherosclerosis. Kardiol Pol. 2014;72:311–314. - PubMed
-
- Combadière C, Potteaux S, Rodero M, Simon T, Pezard A, Esposito B, Merval R, Proudfoot A, Tedgui A, Mallat Z. Combined inhibition of ccl2, cx3cr1, and ccr5 abrogates ly6c(hi) and ly6c(lo) monocytosis and almost abolishes atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice. Circulation. 2008;117:1649–1657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

