The kidney in heart failure: an update
- PMID: 25838436
- PMCID: PMC4465636
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv010
The kidney in heart failure: an update
Abstract
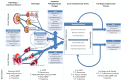
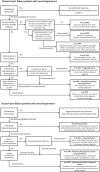
Heart and kidney are closely related in the clinical syndrome of heart failure (HF). It is now sufficiently clear that renal dysfunction occurs frequently in all phenotypes of HF, and when present, it is associated with higher mortality and morbidity. While the pathophysiology is multifactorial, the most important factors are a reduced renal perfusion and venous congestion. Recent interest has focused on worsening renal function (WRF), a situation strongly related to mortality, but seemingly only when HF status deteriorates. Unfortunately, to date clinicians are unable to identify specifically those patients with a grim prognosis following WRF. Although much has been learned on cardiorenal interaction in HF, still more questions have been left unanswered. The coming decade should provide us with more dedicated epidemiologic, mechanistic, and controlled trials in HF patients with reduced renal function. An updated classification of the cardiorenal syndrome that incorporates recent evidence and points towards areas of interest and uncertainties, and areas where progress is needed could facilitate this process. Ultimately, this should lead to preventive and treatment strategies that can preserve renal function and associated outcome in patients with HF.
Keywords: Cardiorenal interaction; Heart failure; Renal dysfunction.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author 2015. For permissions please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Shlipak MG, Massie BM. The clinical challenge of cardiorenal syndrome. Circulation 2004;110:1514–1517. - PubMed
-
- Blake WD, Wegria R, Keating RP, Ward HP. Effect of increased renal venous pressure on renal function. Am J Physiol 1949;157:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Leithe ME, Margorien RD, Hermiller JB, Unverferth DV, Leier CV. Relationship between central hemodynamics and regional blood-flow in normal subjects and in patients with congestive heart-failure. Circulation 1984;69:57–64. - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA, Kellum JA, Haase M, Muller C, Damman K, Murray PT, Cruz D, House AA, Schmidt-Ott KM, Vescovo G, Bagshaw SM, Hoste EA, Briguori C, Braam B, Chawla LS, Costanzo MR, Tumlin JA, Herzog CA, Mehta RL, Rabb H, Shaw AD, Singbartl K, Ronco C; Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Consensus Group. Pathophysiology of the cardiorenal syndromes: executive summary from the Eleventh Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI). Blood Purif 2014;37:2–13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

