Analyzing the antibacterial effects of food ingredients: model experiments with allicin and garlic extracts on biofilm formation and viability of Staphylococcus epidermidis
- PMID: 25838894
- PMCID: PMC4376410
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.199
Analyzing the antibacterial effects of food ingredients: model experiments with allicin and garlic extracts on biofilm formation and viability of Staphylococcus epidermidis
Abstract
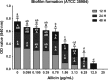
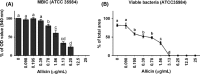
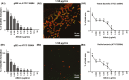
To demonstrate different effects of garlic extracts and their main antibiotic substance allicin, as a template for investigations on the antibacterial activity of food ingredients. Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228 and the isogenic biofilm-forming strain ATCC 35984 were used to compare the activity of allicin against planktonic bacteria and bacterial biofilms. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration (MBIC) for pure allicin were identical and reached at a concentration of 12.5 μg/mL. MBICs for standardized garlic extracts were significantly lower, with 1.56 and 0.78 μg/mL allicin for garlic water and ethanol extract, respectively. Biofilm density was impaired significantly at a concentration of 0.78 μg/mL allicin. Viability staining followed by confocal laser scanning microscopy showed, however, a 100% bactericidal effect on biofilm-embedded bacteria at a concentration of 3.13 μg/mL allicin. qRT-PCR analysis provided no convincing evidence for specific effects of allicin on biofilm-associated genes. Extracts of fresh garlic are more potent inhibitors of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms than pure allicin, but allicin exerts a unique bactericidal effect on biofilm-embedded bacteria. The current experimental protocol has proven to be a valid approach to characterize the antimicrobial activity of traditional food ingredients.
Keywords: ATCC 12228; ATCC 35984; Allicin; Staphylococcus epidermidis; bacterial biofilm.
Figures
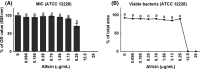

References
-
- Aguirrezábal MM, Mateo J, Domínguez MC. Zumalacárregui JM. The effect of paprika, garlic and salt on rancidity in dry sausages. Meat Sci. 2000;54:77–81. - PubMed
-
- Amagase H. Clarifying the real bioactive constituents of garlic. J. Nutr. 2006;136:716S–725S. - PubMed
-
- Ankri S. Mirelman D. Antimicrobial properties of allicin from garlic. Microbes Infect. 1999;1:125–129. - PubMed
-
- Bachrach G, Jamil A, Naor R, Tal G, Ludmer Z, Steinberg D. Garlic allicin as a potential agent for controlling oral pathogens. J. Med. Food. 2011;14:1338–1343. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

