Orbital Pseudotumor: Uncommon Initial Presentation of IgG4-Related Disease
- PMID: 25838962
- PMCID: PMC4369927
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/324365
Orbital Pseudotumor: Uncommon Initial Presentation of IgG4-Related Disease
Abstract
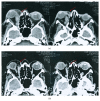
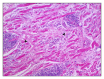
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) encompasses a group of fibroinflammatory conditions recognized in recent times. The main clinical features include variable degrees of tissue fibrosis, tumorlike expansions, perivascular lymphocytic infiltration rich in IgG4-positive plasma cells, and elevated serum IgG4. A case has been reported of an elderly patient with an unexplained unilateral exophthalmia; biopsy was performed and revealed lymphocytic infiltration, suggesting IgG4-RD. High serum levels of IgG4, in association with a good response to steroid therapy and to the exclusion of other diagnoses, confirmed the hypothesis of orbital pseudotumor by IgG4-RD.
Figures

References
-
- Pilar B. Z., Manuel R. C., Xavier B., John H. S. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmunity Reviews. 2014;13(12):1203–1210. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

