Shengmai injection improved doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy by alleviating myocardial endoplasmic reticulum stress and caspase-12 dependent apoptosis
- PMID: 25839043
- PMCID: PMC4369903
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/952671
Shengmai injection improved doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy by alleviating myocardial endoplasmic reticulum stress and caspase-12 dependent apoptosis
Abstract
Background: Apoptosis plays vital roles in the progression of doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy (DOX-CM). Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) could induce specific apoptosis by caspase-12 dependent pathway. Shengmai Injection (SMI), a famous Traditional Chinese Medicine, could alleviate the heart damage via inhibiting myocardial apoptosis. However, it is unknown whether SMI can alleviate ER stress and its specific apoptosis in the setting of DOX-CM.
Objective: To explore the effects of SMI on heart function, myocardial ER stress, and apoptosis of DOX-CM rats.
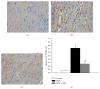
Methods: Rats with DOX-CM were treated by SMI. Heart function was assessed by echocardiography and brain natriuretic peptide. Myocardial apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay. ER stress was assessed by detecting the expressions of GRP78 and caspase-12.
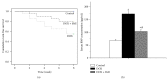
Results: At the end of eight-week, compared to control, significant heart dysfunction happened in DOX group. The ratio of apoptotic cardiomyocytes and the expressions of GRP78 and caspase-12 increased significantly (P < 0.05). Compared to DOX group, the apoptotic ratio and the expressions of GRP78 and caspase-12 significantly decreased in DOX + SMI group (P < 0.05), accompanied with improved heart function.
Conclusion: SMI could alleviate myocardial ER stress and caspase-12 dependent apoptosis, which subsequently helped to improve the heart function of rats with DOX-CM.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A metabolomic study of rats with doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy and Shengmai injection treatment.PLoS One. 2015 May 4;10(5):e0125209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125209. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25938766 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of Astragalus injection on cardiomyocyte apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and expression of connexin in cardiomyopathy rats induced by adriamycin].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Feb 8;34(2):159-163. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.5576.2018.039. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29926682 Chinese.
-
Inhibition of CACNA1H attenuates doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity by affecting endoplasmic reticulum stress.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Dec;120:109475. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109475. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31580970
-
Activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in doxorubicin cardiomyopathy.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2009 Dec;11(6):389-95. doi: 10.1007/s11906-009-0068-8. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2009. PMID: 19895749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy.Cardiology. 2010;115(2):155-62. doi: 10.1159/000265166. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Cardiology. 2010. PMID: 20016174 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo and in vitro protective effects of shengmai injection against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):638-651. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2046801. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35298357 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxic injury, apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress by suppressing glucose regulated protein 78 (GRP78)-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):844-855. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2013109. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 34898378 Free PMC article.
-
A review of chemotherapeutic drugs-induced arrhythmia and potential intervention with traditional Chinese medicines.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 20;15:1340855. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1340855. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38572424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Quantitative Serum Proteomic Analysis Helps to Explore the Comprehensive Mechanism and Identify Serum Biomarkers of Shengmai Injection's Effect on Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Ischemia in Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 28;12:666429. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.666429. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33995093 Free PMC article.
-
Glibenclamide exacerbates adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity by activating oxidative stress-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Apr;15(4):3425-3431. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5862. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29545864 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

