Interleukin-21 sustains inflammatory signals that contribute to sporadic colon tumorigenesis
- PMID: 25839161
- PMCID: PMC4496406
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3532
Interleukin-21 sustains inflammatory signals that contribute to sporadic colon tumorigenesis
Abstract
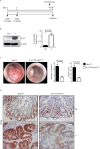
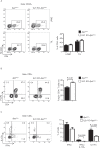
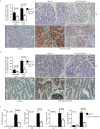
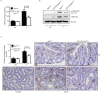
Interleukin (IL)-21 triggers inflammatory signals that contribute to the growth of neoplastic cells in mouse models of colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CRC). Because most CRCs are sporadic and arise in the absence of overt inflammation we have investigated the role of IL-21 in these tumors in mouse and man. IL-21 was highly expressed in human sporadic CRC and produced mostly by IFN-γ-expressing T-bet/RORγt double-positive CD3+CD8- cells. Stimulation of human CRC cell lines with IL-21 did not directly activate the oncogenic transcription factors STAT3 and NF-kB and did not affect CRC cell proliferation and survival. In contrast, IL-21 modulated the production of protumorigenic factors by human tumor infiltrating T cells. IL-21 was upregulated in the neoplastic areas, as compared with non-tumor mucosa, of Apc(min/+) mice, and genetic ablation of IL-21 in such mice resulted in a marked decrease of both tumor incidence and size. IL-21 deficiency was associated with reduced STAT3/NF-kB activation in both immune cells and neoplastic cells, diminished synthesis of protumorigenic cytokines (that is, IL-17A, IL-22, TNF-α and IL-6), downregulation of COX-2/PGE2 pathway and decreased angiogenesis in the lesions of Apc(min/+) mice. Altogether, data suggest that IL-21 promotes a protumorigenic inflammatory circuit that ultimately sustains the development of sporadic CRC.
Keywords: Apcmin/+ mice; COX-2/PGE2; STAT3; VEGF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Fearon ER, Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990;61(5):759–767. - PubMed
-
- Huber S, Gagliani N, Zenewicz LA, Huber FJ, Bosurgi L, Hu B, Hedl M, Zhang W, O'Connor W, Jr, Murphy AJ, Valenzuela DM, Yancopoulos GD, Booth CJ, Cho JH, Ouyang W, Abraham C, et al. IL-22BP is regulated by the inflammasome and modulates tumorigenesis in the intestine. Nature. 2012;491(7423):259–263. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hyun YS, Han DS, Lee AR, Eun CS, Youn J, Kim HY. Role of IL-17A in the development of colitis-associated cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33(4):931–936. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

