Role of interleukin-1 receptor signaling in the behavioral effects of ethanol and benzodiazepines
- PMID: 25839897
- PMCID: PMC4465986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.03.015
Role of interleukin-1 receptor signaling in the behavioral effects of ethanol and benzodiazepines
Abstract
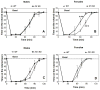
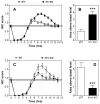
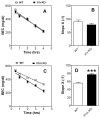
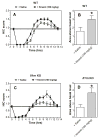
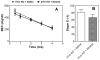
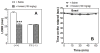
Gene expression studies identified the interleukin-1 receptor type I (IL-1R1) as part of a pathway associated with a genetic predisposition to high alcohol consumption, and lack of the endogenous IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) strongly reduced ethanol intake in mice. Here, we compared ethanol-mediated behaviors in mice lacking Il1rn or Il1r1. Deletion of Il1rn (the gene encoding IL-1ra) increases sensitivity to the sedative/hypnotic effects of ethanol and flurazepam and reduces severity of acute ethanol withdrawal. Conversely, deletion of Il1r1 (the gene encoding the IL-1 receptor type I, IL-1R1) reduces sensitivity to the sedative effects of ethanol and flurazepam and increases the severity of acute ethanol withdrawal. The sedative effects of ketamine and pentobarbital were not altered in the knockout (KO) strains. Ethanol intake and preference were not changed in mice lacking Il1r1 in three different tests of ethanol consumption. Recovery from ethanol-induced motor incoordination was only altered in female mice lacking Il1r1. Mice lacking Il1rn (but not Il1r1) showed increased ethanol clearance and decreased ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion. The increased ethanol- and flurazepam-induced sedation in Il1rn KO mice was decreased by administration of IL-1ra (Kineret), and pre-treatment with Kineret also restored the severity of acute ethanol withdrawal. Ethanol-induced sedation and withdrawal severity were changed in opposite directions in the null mutants, indicating that these responses are likely regulated by IL-1R1 signaling, whereas ethanol intake and preference do not appear to be solely regulated by this pathway.
Keywords: Alcohol withdrawal; Anakinra; Conditioned taste aversion; Drinking in the dark; Flurazepam; IL-1R1; IL-1ra; Il1r1; Il1rn; Kineret; Knockout mice; Loss of righting reflex; Two-bottle choice.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

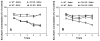


Similar articles
-
Ethanol-related behaviors in mice lacking the sigma-1 receptor.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Jan 15;297:196-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.10.013. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26462569 Free PMC article.
-
Role of endocannabinoids in alcohol consumption and intoxication: studies of mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007 Jul;32(7):1570-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301274. Epub 2006 Dec 13. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17164820
-
Hepatocyte-specific deletion of IL1-RI attenuates liver injury by blocking IL-1 driven autoinflammation.J Hepatol. 2018 May;68(5):986-995. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.01.008. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29366909
-
Deficiency of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist (DIRA): Report of the First Indian Patient and a Novel Deletion Affecting IL1RN.J Clin Immunol. 2017 Jul;37(5):445-451. doi: 10.1007/s10875-017-0399-1. Epub 2017 May 15. J Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28503715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of physical dependence on alcohol in rodents.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;56:311-25. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7529-6_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975. PMID: 807086 Review.
Cited by
-
From adolescence to late aging: A comprehensive review of social behavior, alcohol, and neuroinflammation across the lifespan.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;148:231-303. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31733665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age- and cytokine-dependent modulation of GABAergic transmission within the basolateral amygdala of male Sprague Dawley rats.Neuropharmacology. 2025 Apr 1;267:110304. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2025.110304. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Neuropharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39827996
-
Sedative and Motor Incoordination Effects of Ethanol in Mice Lacking CD14, TLR2, TLR4, or MyD88.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2017 Mar;41(3):531-540. doi: 10.1111/acer.13314. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2017. PMID: 28160299 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling reveals a lingering effect of prenatal alcohol exposure on inflammatory-related genes during adolescence and adulthood.Cytokine. 2020 Sep;133:155126. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155126. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 32505093 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimmune signaling in alcohol use disorder.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2019 Feb;177:34-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2018.12.007. Epub 2018 Dec 24. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2019. PMID: 30590091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bajo M, Herman MA, Varodayan FP, Oleata CS, Madamba SG, Harris RA, Blednov YA, Roberto M. Role of the IL-1 receptor antagonist in ethanol-induced regulation of GABAergic transmission in the central amygdala. Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Dec 3; doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.11.011. pii: S0889–1591(14)00555-8. [Epub ahead of print] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becker HC, Veatch LM, Diaz-Granados JL. Repeated ethanol withdrawal experience selectively alters sensitivity to different chemoconvulsant drugs in mice. Psychopharmacology. 1998;139:145–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

