Laser system refinements to reduce variability in infarct size in the rat photothrombotic stroke model
- PMID: 25840363
- PMCID: PMC4490890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.03.029
Laser system refinements to reduce variability in infarct size in the rat photothrombotic stroke model
Abstract
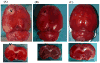
Background: The rat photothrombotic stroke model can induce brain infarcts with reasonable biological variability. Nevertheless, we observed unexplained high inter-individual variability despite using a rigorous protocol. Of the three major determinants of infarct volume, photosensitive dye concentration and illumination period were strictly controlled, whereas undetected fluctuation in laser power output was suspected to account for the variability.
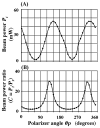
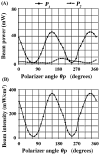
New method: The frequently utilized Diode Pumped Solid State (DPSS) lasers emitting 532 nm (green) light can exhibit fluctuations in output power due to temperature and input power alterations. The polarization properties of the Nd:YAG and Nd:YVO4 crystals commonly used in these lasers are another potential source of fluctuation, since one means of controlling output power uses a polarizer with a variable transmission axis. Thus, the properties of DPSS lasers and the relationship between power output and infarct size were explored.
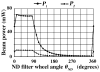
Results: DPSS laser beam intensity showed considerable variation. Either a polarizer or a variable neutral density filter allowed adjustment of a polarized laser beam to the desired intensity. When the beam was unpolarized, the experimenter was restricted to using a variable neutral density filter.
Comparison with existing method(s): Our refined approach includes continuous monitoring of DPSS laser intensity via beam sampling using a pellicle beamsplitter and photodiode sensor. This guarantees the desired beam intensity at the targeted brain area during stroke induction, with the intensity controlled either through a polarizer or variable neutral density filter.
Conclusions: Continuous monitoring and control of laser beam intensity is critical for ensuring consistent infarct size.
Keywords: Continuous monitoring of laser intensity; DPSS laser stability; Intensity adjustments; Laser beam polarization; Photothrombotic stroke; Variability.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
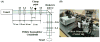

References
-
- Alaverdashvili M, Moon SK, Beckman CD, Virag A, Whishaw IQ. Acute but not chronic differences in skilled reaching for food following motor cortex devascularization vs. photothrombotic stroke in the rat. Neuroscience. 2008;157:297–308. - PubMed
-
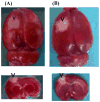
- Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski HM. Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke. 1986;17:1304–8. - PubMed
-
- Born M, Wolf E. Principles of optics: electromagnetic theory of propagation, interference and diffraction of light. 7. UK: Cambridge University Press; 1999.
-
- Byer RL. Diode laser—pumped solid-state lasers. Science. 1988;239:742–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

