NGF-induced TrkA/CD44 association is involved in tumor aggressiveness and resistance to lestaurtinib
- PMID: 25840418
- PMCID: PMC4496399
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3227
NGF-induced TrkA/CD44 association is involved in tumor aggressiveness and resistance to lestaurtinib
Abstract
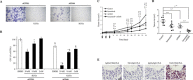
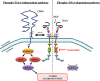
There is accumulating evidence that TrkA and its ligand Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) are involved in cancer development. Staurosporine derivatives such as K252a and lestaurtinib have been developed to block TrkA kinase signaling, but no clinical trial has fully demonstrated their therapeutic efficacy. Therapeutic failures are likely due to the existence of intrinsic signaling pathways in cancer cells that impede or bypass the effects of TrkA tyrosine kinase inhibitors. To verify this hypothesis, we combined different approaches including mass spectrometry proteomics, co-immunoprecipitation and proximity ligation assays. We found that NGF treatment induced CD44 binding to TrkA at the plasma membrane and subsequent activation of the p115RhoGEF/RhoA/ROCK1 pathway to stimulate breast cancer cell invasion. The NGF-induced CD44 signaling was independent of TrkA kinase activity. Moreover, both TrkA tyrosine kinase inhibition with lestaurtinib and CD44 silencing with siRNA inhibited cell growth in vitro as well as tumor development in mouse xenograft model; combined treatment significantly enhanced the antineoplastic effects of either treatment alone. Altogether, our results demonstrate that NGF-induced tyrosine kinase independent TrkA signaling through CD44 was sufficient to maintain tumor aggressiveness. Our findings provide an alternative mechanism of cancer resistance to lestaurtinib and indicate that dual inhibition of CD44 and TrkA tyrosine kinase activity may represent a novel therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: CD44; NGF; TrkA; lestaurtinib; resistance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct interaction of TrkA/CD44v3 is essential for NGF-promoted aggressiveness of breast cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 28;41(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02314-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35346305 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Abl tyrosine kinase enhances nerve growth factor-mediated signaling in Bcr-Abl transformed cells via the alteration of signaling complex and the receptor turnover.Oncogene. 2008 Aug 7;27(34):4678-89. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.107. Epub 2008 Apr 21. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18427551
-
Type I interferons up-regulate the expression and signalling of p75 NTR/TrkA receptor complex in differentiated human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:321-34. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24333329
-
NGF and ProNGF: Regulation of neuronal and neoplastic responses through receptor signaling.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 May;58:16-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.11.003. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25491371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NGF/TrkA Signaling as a Therapeutic Target for Pain.Pain Pract. 2016 Feb;16(2):175-82. doi: 10.1111/papr.12342. Epub 2015 Aug 27. Pain Pract. 2016. PMID: 26452158 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer stem cells-driven tumor growth and immune escape: the Janus face of neurotrophins.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Dec 7;11(23):11770-11792. doi: 10.18632/aging.102499. Epub 2019 Dec 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31812953 Free PMC article.
-
Direct interaction of TrkA/CD44v3 is essential for NGF-promoted aggressiveness of breast cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 28;41(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02314-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35346305 Free PMC article.
-
β-Lapachone Exerts Anticancer Effects by Downregulating p53, Lys-Acetylated Proteins, TrkA, p38 MAPK, SOD1, Caspase-2, CD44 and NPM in Oxaliplatin-Resistant HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 7;24(12):9867. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129867. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373014 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve Growth Factor Modulates Regulatory Cell Volume Behavior via Stimulating TRPV1, TRPM8 Channels and Inducing Ca2+ Signaling in Human Conjunctival Epithelial Cells.Cells. 2025 May 15;14(10):719. doi: 10.3390/cells14100719. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40422222 Free PMC article.
-
TGFβ2-induced formation of lipid droplets supports acidosis-driven EMT and the metastatic spreading of cancer cells.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 23;11(1):454. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14262-3. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31974393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adriaenssens E, Vanhecke E, Saule P, Mougel A, Page A, Romon R, Nurcombe V, Le Bourhis X, Hondermarck H. Nerve growth factor is a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer research. 2008;68:346–351. - PubMed
-
- Bloom AP, Jimenez-Andrade JM, Taylor RN, Castaneda-Corral G, Kaczmarska MJ, Freeman KT, Coughlin KA, Ghilardi JR, Kuskowski MA, Mantyh PW. Breast cancer-induced bone remodeling, skeletal pain, and sprouting of sensory nerve fibers. The journal of pain: official journal of the American Pain Society. 2011;12:698–711. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marchesi F, Piemonti L, Mantovani A, Allavena P. Molecular mechanisms of perineural invasion, a forgotten pathway of dissemination and metastasis. Cytokine & growth factor reviews. 2010;21:77–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

