Dual targeting of microtubule and topoisomerase II by α-carboline derivative YCH337 for tumor proliferation and growth inhibition
- PMID: 25840421
- PMCID: PMC4496195
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3264
Dual targeting of microtubule and topoisomerase II by α-carboline derivative YCH337 for tumor proliferation and growth inhibition
Abstract
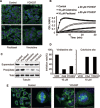
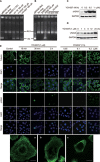
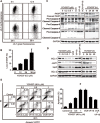
Both microtubule and topoisomerase II (Top2) are important anticancer targets and their respective inhibitors are widely used in combination for cancer therapy. However, some combinations could be mutually antagonistic and drug resistance further limits their therapeutic efficacy. Here we report YCH337, a novel α-carboline derivative that targets both microtubule and Top2, eliciting tumor proliferation and growth inhibition and overcoming drug resistance. YCH337 inhibited microtubule polymerization by binding to the colchicine site and subsequently led to mitotic arrest. It also suppressed Top2 and caused DNA double-strand breaks. It disrupted microtubule more potently than Top2. YCH337 induced reversible mitotic arrest at low concentrations but persistent DNA damage. YCH337 caused intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis and decreased MCL-1, cIAP1 and XIAP proteins. In this aspect, YCH337 behaved differently from the combination of vincristine and etoposide. YCH337 inhibited proliferation of tumor cells with an averaged IC50 of 0.3 μM. It significantly suppressed the growth of HT-29 xenografts in nude mice too. Importantly, YCH337 nearly equally killed different-mechanism-mediated resistant tumor cells and corresponding parent cells. Together with the novelty of its chemical structure, YCH337 could serve as a promising lead for drug development and a prototype for a dual microtubule/Top2 targeting strategy for cancer therapy.
Keywords: YCH337; antitumor activity; microtubule; topoisomerase II; α-carboline derivative.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Jackson JR, Patrick DR, Dar MM, Huang PS. Targeted anti-mitotic therapies: can we improve on tubulin agents? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Kavallaris M. Microtubules and resistance to tubulin-binding agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:194–204. - PubMed
-
- Kufe DW PR, Weichselbaum RR, Bast RC, Gansler TS, Holland JF, et al., editors. Part VI Cancer Management. Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine. 6th ed. Vol. 2. Hamilton: BC Decker; 2003. pp. 1195–2290.
-
- Kaur R, Kaur G, Gill RK, Soni R, Bariwal J. Recent developments in tubulin polymerization inhibitors: An overview. Eur J Med Chem. 2014;87C:89–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

