Two-Component-System Histidine Kinases Involved in Growth of Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e at Low Temperatures
- PMID: 25841007
- PMCID: PMC4524140
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00626-15
Two-Component-System Histidine Kinases Involved in Growth of Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e at Low Temperatures
Abstract
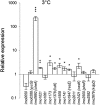
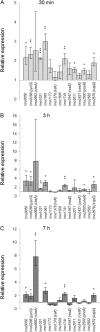
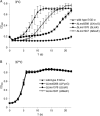
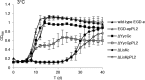
Two-component systems (TCSs) aid bacteria in adapting to a wide variety of stress conditions. While the role of TCS response regulators in the cold tolerance of the psychrotrophic foodborne pathogen Listeria monocytogenes has been demonstrated previously, no comprehensive studies showing the role of TCS histidine kinases of L. monocytogenes at low temperature have been performed. We compared the expression levels of each histidine kinase-encoding gene of L. monocytogenes EGD-e in logarithmic growth phase at 3°C and 37°C, as well as the expression levels 30 min, 3 h, and 7 h after cold shock at 5°C and preceding cold shock (at 37°C). We constructed a deletion mutation in each TCS histidine kinase gene, monitored the growth of the EGD-e wild-type and mutant strains at 3°C and 37°C, and measured the minimum growth temperature of each strain. Two genes, yycG and lisK, proved significant in regard to induced relative expression levels under cold conditions and cold-sensitive mutant phenotypes. Moreover, the ΔresE mutant showed a lower growth rate than that of wild-type EGD-e at 3°C. Eleven other genes showed upregulated gene expression but revealed no cold-sensitive phenotypes. The results show that the histidine kinases encoded by yycG and lisK are important for the growth and adaptation of L. monocytogenes EGD-e at low temperature.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Screening of the two-component-system histidine kinases of Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e. LiaS is needed for growth under heat, acid, alkali, osmotic, ethanol and oxidative stresses.Food Microbiol. 2017 Aug;65:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.01.018. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Food Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28400017
-
Genes encoding putative DEAD-box RNA helicases in Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e are needed for growth and motility at 3°C.Environ Microbiol. 2012 Aug;14(8):2223-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02761.x. Epub 2012 May 7. Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22564273
-
Contributions of two-component regulatory systems, alternative sigma factors, and negative regulators to Listeria monocytogenes cold adaptation and cold growth.J Food Prot. 2008 Feb;71(2):420-5. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-71.2.420. J Food Prot. 2008. PMID: 18326199 Free PMC article.
-
Physiology and genetics of Listeria monocytogenes survival and growth at cold temperatures.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2009 Mar;49(3):237-53. doi: 10.1080/10408390701856272. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19093268 Review.
-
Cold stress tolerance of Listeria monocytogenes: A review of molecular adaptive mechanisms and food safety implications.J Food Prot. 2006 Jun;69(6):1473-84. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-69.6.1473. J Food Prot. 2006. PMID: 16786878 Review.
Cited by
-
Disinfectant Susceptibility of Biofilm Formed by Listeria monocytogenes under Selected Environmental Conditions.Microorganisms. 2019 Aug 21;7(9):280. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7090280. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31438656 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of Listeria monocytogenes to Stress Conditions Encountered in Food and Food Processing Environments.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 13;9:2700. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02700. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30555426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic determinants in Listeria monocytogenes anaerobic listeriolysin O production.Arch Microbiol. 2017 Aug;199(6):827-837. doi: 10.1007/s00203-017-1355-4. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Arch Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28289786 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Genome Sequence of Qipengyuania sediminis CGMCC 1.12928T, Shed Light on Its Role in Matter-Cycle and Cold Adaption Mechanism of the Genus Qipengyuania.Curr Microbiol. 2019 Sep;76(9):988-994. doi: 10.1007/s00284-019-01712-w. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Curr Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31172271
-
Role of Efflux Pumps in the in vitro Development of Ciprofloxacin Resistance in Listeria monocytogenes.Front Microbiol. 2018 Sep 27;9:2350. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02350. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30319598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Autio T, Hielm S, Miettinen M, Sjöberg A-M, Aarnisalo K, Björkroth J, Mattila-Sandholm T, Korkeala H. 1999. Sources of Listeria monocytogenes contamination in a cold-smoked rainbow trout processing plant detected by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:150–155. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berzins A, Hellström S, Silins I, Korkeala H. 2010. Contamination patterns of Listeria monocytogenes in cold-smoked pork processing. J Food Prot 73:2103–2109. - PubMed
-
- Keto-Timonen R, Tolvanen R, Lundén J, Korkeala H. 2007. An 8-year surveillance of the diversity and persistence of Listeria monocytogenes in a chilled food processing plant analyzed by amplified fragment length polymorphism. J Food Prot 70:1866–1873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

