Vagotomy reverses established allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity to methacholine in the mouse
- PMID: 25842220
- PMCID: PMC4827162
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2015.03.007
Vagotomy reverses established allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity to methacholine in the mouse
Abstract
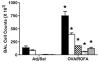
We evaluated the role of vagal reflexes in a mouse model of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. Mice were actively sensitized to ovalbumin then exposed to the allergen via inhalation. Prior to ovalbumin inhalation, mice also received intratracheally-instilled particulate matter in order to boost the allergic response. In control mice, methacholine (i.v.) caused a dose-dependent increase in respiratory tract resistance (RT) that only modestly decreased if the vagi were severed bilaterally just prior to the methacholine challenge. Sensitized and challenged mice, however, manifested an airway reactivity increase that was abolished by severing the vagi prior to methacholine challenge. In an innervated ex vivo mouse lung model, methacholine selectively evoked action potential discharge in a subset of distension-sensitive A-fibers. These data support the hypothesis that the major component of the increased airway reactivity in inflamed mice is due to a vagal reflex initiated by activation of afferent fibers, even in response to a direct (i.e., smooth muscle)-acting muscarinic agonist.
Keywords: Airway hyperreactivity; Allergic inflammation; Particulate matter; Reflex; Vagotomy; Vagus nerve.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

References
-
- Canning BJ. Reflex regulation of airway smooth muscle tone. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006:00313. - PubMed
-
- Chuaychoo B, Hunter DD, Myers AC, Kollarik M, Undem BJ. Allergen-induced substance P synthesis in large-diameter sensory neurons innervating the lungs. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005;116:325–331. - PubMed
-
- Costello RW, Evans CM, Yost BL, Belmonte KE, Gleich GJ, Jacoby DB, Fryer AD. Antigen-induced hyperreactivity to histamine: role of the vagus nerves and eosinophils. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 1999;276:L709–L714. - PubMed
-
- Fryer AD, Wills-Karp M. Dysfunction of M2-muscarinic receptors in pulmonary parasympathetic nerves after antigen challenge. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991;71:2255–2261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

