Quinine for muscle cramps
- PMID: 25842375
- PMCID: PMC11055607
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005044.pub3
Quinine for muscle cramps
Abstract
Background: Muscle cramps can occur anywhere and for many reasons. Quinine has been used to treat cramps of all causes. However, controversy continues about its efficacy and safety. This review was first published in 2010 and searches were updated in 2014.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy and safety of quinine-based agents in treating muscle cramps.
Search methods: On 27 October 2014 we searched the Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Group Specialized Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE and EMBASE. We searched reference lists of articles up to 2014. We also searched for ongoing trials in November 2014.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials of people of all ages with muscle cramps in any location and of any cause, treated with quinine or its derivatives.
Data collection and analysis: Three review authors independently selected trials for inclusion, assessed risk of bias and extracted data. We contacted study authors for additional information. For comparisons including more than one trial, we assessed the quality of the evidence using Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE).
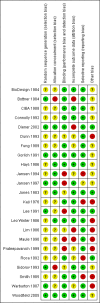
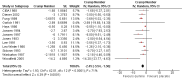
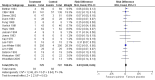
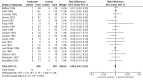
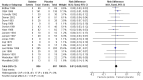
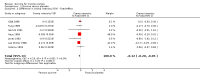
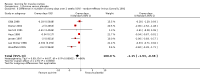
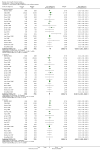
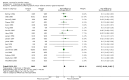
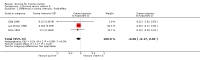
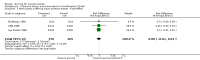
Main results: We identified 23 trials with a total of 1586 participants. Fifty-eight per cent of these participants were from five unpublished studies. Quinine was compared to placebo (20 trials, n = 1140), vitamin E (four trials, n = 543), a quinine-vitamin E combination (three trials, n = 510), a quinine-theophylline combination (one trial, n = 77), and xylocaine injections into the gastrocnemius muscle (one trial, n = 24). The most commonly used quinine dosage was 300 mg/day (range 200 to 500 mg). We found no new trials for inclusion when searches were updated in 2014.The risk of bias in the trials varied considerably. All 23 trials claimed to be randomised, but only a minority described randomisation and allocation concealment adequately.Compared to placebo, quinine significantly reduced cramp number over two weeks by 28%, cramp intensity by 10%, and cramp days by 20%. Cramp duration was not significantly affected.A significantly greater number of people suffered minor adverse events on quinine than placebo (risk difference (RD) 3%, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0% to 6%), mainly gastrointestinal symptoms. Overdoses of quinine have been reported elsewhere to cause potentially fatal adverse effects, but in the included trials there was no significant difference in major adverse events compared with placebo (RD 0%, 95% CI -1% to 2%). One participant suffered from thrombocytopenia (0.12% risk) on quinine.A quinine-vitamin E combination, vitamin E alone, and xylocaine injections into gastrocnemius were not significantly different to quinine across all outcomes, including adverse effects. Based on a single trial comparison, quinine alone was significantly less effective than a quinine-theophylline combination but with no significant differences in adverse events.
Authors' conclusions: There is low quality evidence that quinine (200 mg to 500 mg daily) significantly reduces cramp number and cramp days and moderate quality evidence that quinine reduces cramp intensity. There is moderate quality evidence that with use up to 60 days, the incidence of serious adverse events is not significantly greater than for placebo in the identified trials, but because serious adverse events can be rarely fatal, in some countries prescription of quinine is severely restricted.Evidence from single trials suggests that theophylline combined with quinine improves cramps more than quinine alone, and the effects of xylocaine injections into gastrocnemius are not significantly different to quinine across all outcomes. Low or moderate quality evidence shows no significant difference between quinine and vitamin E or quinine and quinine-vitamin E mixture. Further research into these alternatives, as well other pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments, is thus warranted.There is no evidence to judge optimal dosage or duration of quinine treatment. Further studies using different dosages and measurement of serum quinine levels will allow a therapeutic range to be defined for muscle cramp. Because serious adverse events are not common, large population studies are required to more accurately inform incidence. Longer lengths of follow-up in future trials will help determine the duration of action following cessation of quinine as well as long-term adverse events. The search for new therapies, pharmacological and nonpharmacological, should continue and further trials should compare vitamin E, quinine-vitamin E combination, and quinine-theophylline mixture with quinine.
Conflict of interest statement
Ruth Brassington is Managing Editor of the Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Group and Michael Lunn is Joint Co‐ordinating Editor. He was not involved in acceptance of the review for publication.
There are no potential conflicts of interest.
Tariq El‐Tawil: Author deceased; declaration of interest published in the protocol: “No potential conflicts of interest".
Figures

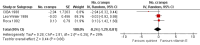
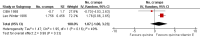














Update of
-
Quinine for muscle cramps.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Dec 8;(12):CD005044. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005044.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 05;(4):CD005044. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005044.pub3. PMID: 21154358 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
BioDesign 1984 {unpublished data only}
-
- BioDesign (for Bio Products Inc.). Clinical evaluation of Q‐Vel® in patients with nocturnal leg muscle cramps. Federal Register, Docket No. 77N‐0094. 1984.
Bottner 1984 {unpublished data only}
-
- Bottner M (for Scholl Inc.). Clinical trial of the efficacy of quinine sulphate in the treatment of nocturnal leg muscle cramps. Federal Register, Docket No. 77N‐0094. 1984.
CIBA 1988 {unpublished data only}
-
- CIBA Consumer Pharmaceuticals. A short‐term randomized, double‐blind parallel study of Q‐Vel® versus quinine sulfate versus vitamin E versus placebo in the prevention and treatment of nocturnal leg cramps. Federal Register, Docket No. 77N‐0094. 1988.
Connolly 1992 {published data only}
-
- Connolly PS, Shirley EA, Wasson JH, Nierenberg DW. Treatment of nocturnal leg cramps. A crossover trial of quinine vs vitamin E. Archives of Internal Medicine 1992;152(9):1877‐80. [PUBMED: 1520054] - PubMed
Diener 2002 {published data only}
-
- Diener HC, Dethlefsen U, Dethlefsen‐Gruber S, Verbeek P. Effectiveness of quinine in treating muscle cramps: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group, multicentre trial. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2002;56(4):243‐6. [PUBMED: 12074203] - PubMed
Dunn 1993 {published data only}
Fung 1989 {published data only}
Gorlich 1991 {published data only}
-
- Gorlich HD, Gablenz E, Steinberg HW. Treatment of nocturnal leg cramps. A multicenter, double blind, placebo controlled comparison between the combination of quinine and theophylline ethylene diamine with quinine. Arzneimittel‐Forschung 1991;41(2):167‐75. [PUBMED: 2043179] - PubMed
Hays 1986 {unpublished data only}
-
- Hays RM, Goodman JJ (for Scholl Inc.). Clinical trial of the efficacy of quinine sulfate in the treatment of nocturnal leg muscle cramps. Federal Register, Docket No. 77N‐0094. 1986.
Jansen 1994 {published data only}
-
- Jansen PH, Veenhuizen KC, Verbeek AL, Straatman H. Efficacy of hydroquinine in preventing frequent ordinary muscle cramp outlasts actual administration. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1994;122(2):157‐61. [PUBMED: 8021700] - PubMed
Jansen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jansen PH, Veenhuizen KC, Wesseling AI, Boo T, Verbeek AL. Randomised controlled trial of hydroquinine in muscle cramps. Lancet 1997;349(9051):528‐32. [PUBMED: 9048790] - PubMed
Jones 1983 {published data only}
-
- Jones K, Castleden CM. A double‐blind comparison of quinine sulphate and placebo in muscle cramps. Age and Ageing 1983;12(2):155‐8. [PUBMED: 6346830] - PubMed
Kaji 1976 {published data only}
-
- Kaji DM, Ackad A, Nottage WG, Stein RM. Prevention of muscle cramps in haemodialysis patients by quinine sulphate. Lancet 1976;2(7976):66‐7. [PUBMED: 59150] - PubMed
Lee 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lee FY, Lee SD, Tsai YT, Lai KH, Chao Y, Lin HC, et al. A randomized controlled trial of quinidine in the treatment of cirrhotic patients with muscle cramps. Journal of Hepatology 1991;12(2):236‐40. [PUBMED: 2051002] - PubMed
Leo Winter 1986 {unpublished data only}
-
- Leo Winter Associates Inc (for Bio Products Inc.). Double blind randomized crossover study of Q‐Vel® versus quinine sulfate versus vitamin E versus placebo in the treatment of nocturnal leg muscle cramps. Federal Register, Docket No. 77N‐0094. 1986.
Lim 1986 {published data only}
-
- Lim SH. Randomised double‐blind trial of quinine sulphate for nocturnal leg cramp. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1986;40(11):462. [PUBMED: 3307858] - PubMed
Maule 1990 {published data only}
-
- Maule B. Nocturnal cramp: quinine versus folklore. Practitioner 1990;234(1487):420‐1. [PUBMED: 2367299] - PubMed
Prateepavanich 1999 {published data only}
-
- Prateepavanich P, Kupniratsaikul V, Charoensak T. The relationship between myofascial trigger points of gastrocnemius muscle and nocturnal calf cramps. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 1999;82(5):451‐9. [PUBMED: 10443094] - PubMed
Roca 1992 {published data only}
-
- Roca AO, Jarjoura D, Blend D, Cugino A, Rutecki GW, Nuchikat PS, et al. Dialysis leg cramps. Efficacy of quinine versus vitamin E. ASAIO Journal 1992;38(3):M481‐5. [PUBMED: 1457907] - PubMed
Sidorov 1993 {published data only}
-
- Sidorov J. Quinine sulfate for leg cramps: does it work?. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1993;41(5):498‐500. [PUBMED: 8486881] - PubMed
Smith 1985 {published data only}
-
- Smith C, Jee R, O'Neill C, Dobbs SM. Double‐blind, placebo controlled, cross‐over study of maintenance treatment with quinine bisulphate for night cramps. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1986;21(1):108P.
Warburton 1987 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Baltodano 1988 {published data only}
-
- Baltodano N, Gallo BV, Weidler DJ. Verapamil vs quinine in recumbent nocturnal leg cramps in the elderly. Archives of Internal Medicine 1988;148(9):1969‐70. - PubMed
Coppin 2005 {published data only}
Morl 1980 {published data only}
-
- Morl H, Dieterich HA. Nocturnal leg cramps‐ their causes and treatment. Medizinische Klinik 1980;75(7):264‐67. - PubMed
Sandoval 1980 {published data only}
-
- Sandoval Pandero J, Perez Garcia A, Martin Abad L, Piqueras A, Garces L, Chacon JC, et al. Action of quinine sulphate on the incidence of muscle cramps during hemodialysis. Medicina Clinica (Barcelona) 1980;75(6):247‐9. - PubMed
Wessely 1984 {published data only}
-
- Wessely S, Dieterich HA. Quinine sulfate plus aminophylline in treatment of muscle cramps in dialysis patients. Therapiewoche 1984;34(29):4356‐9.
Additional references
AAP 2001
-
- Committee on Drugs, American Academy of Pediatrics. The transfer of drugs and other chemicals into human milk. Pediatrics 2001;108(3):776‐89. - PubMed
Abdulla 1999
-
- Abdulla AJ, Jones PW, Pearce VR. Leg cramps in the elderly: prevalence, drug and disease associations. International Journal of Clinical Practice 1999;53(7):494‐6. - PubMed
Abrams 1996
-
- Abrams GA, Concato J, Fallon MB. Muscle cramps in patients with cirrhosis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1996;91(7):1363‐6. - PubMed
Angeli 1996
-
- Angeli P, Albino G, Carraro P, Dalla Pria M, Merkel C, Caregaro L, et al. Cirrhosis and muscle cramps: evidence of a causal relationship. Hepatology 1996;23(2):264‐73. - PubMed
Ayres 1969
Ayres 1974
-
- Ayres S Jr, Mihan R. Nocturnal leg cramps (systremma): a progress report on response to vitamin E. Southern Medical Journal 1974;67(11):1308‐12. - PubMed
Baldissera 1994
-
- Baldissera F, Cavallari P, Dworzak F. Motor neuron 'bistability'. A pathogenetic mechanism for cramps and myokymia. Brain 1994;117(Pt 5):929‐39. - PubMed
Barr 1990
Bateman 1985
-
- Bateman DN, Blain PG, Woodhouse KW, Rawlins MD, Dyson H, Heyworth R, et al. Pharmacokinetics and clinical toxicity of quinine overdosage: lack of efficacy of techniques intended to enhance elimination. Quarterly Journal of Medicine 1985;54(214):125‐31. - PubMed
Berlin 1975
-
- Berlin CM, Stackman JM, Vesell ES. Quinine‐induced alterations in drug disposition. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1975;18(6):670‐9. - PubMed
Blyton 2012
BNF 2010
-
- Joint Formulary Committee. British National Formulary. 9th Edition. London: British Medical Association and Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain, 2010.
Butler 2002
Chou 1985
-
- Chou CT, Wasserstein A, Schumacher HR Jr, Fernandez P. Musculoskeletal manifestations in hemodialysis patients. Journal of Rheumatology 1985;12(6):1149‐53. - PubMed
Dahle 1995
-
- Dahle LO, Berg G, Hammar M, Hurtig M, Larsson L. The effect of oral magnesium substitution on pregnancy‐induced leg cramps. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1995;173(1):175‐80. - PubMed
Eaton 1989
-
- Eaton JM. Is this really a muscle cramp?. Postgraduate Medical Journal 1989;86(3):227‐32. - PubMed
FDA 1982
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Advance notice of proposed rulemaking to reopen the rulemaking for OTC internal analgesic, antipyretic, and antirheumatic drug products. Federal Register Oct 1, 1982; Vol. Docket No: 47 FR 43562:Sec 330.10(a).
FDA 1994
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Drug Products for the Treatment and/or Prevention of Nocturnal Leg Muscle Cramps for Over‐the‐Counter Human Use; Final Rule. Federal Register, Docket No. 77N‐0094 Aug 22, 1994.
FDA 1995a
-
- Food, Drug Administration. FDA orders stop to marketing of quinine for night leg cramps. FDA Homepage www.fda.gov (accessed 20 July 2008).
FDA 1995b
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Drug products containing quinine for the treatment and/or prevention of malaria for over‐the‐counter human use; proposed rule. Federal Register 19 April 1995;60:19649‐55.
FDA 2006
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Quinine: important warning. www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/news/2006/new01521 12 December 2006 (accessed 20 July 2008).
Garrison 2012
Goodman 2001
-
- Goodman L, Gilman A. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th Edition. New York: McGraw‐Hill, 2001.
Gootnick 1943
-
- Gootnick A. Night cramps and quinine. Archives of Internal Medicine 1943;71(4):555‐62.
Guay 2008
-
- Guay DR. Are there alternatives to the use of quinine to treat nocturnal leg cramps?. Consultant Pharmacist 2008;23(2):141‐56. - PubMed
Hallegraeff 2012
-
- Hallegraeff JM, Schans CP, Ruiter R, Greef MH. Stretching before sleep reduces the frequency and severity of nocturnal leg cramps in older adults: a randomised trial. Journal of Physiotherapy 2012;58(1):17‐22. - PubMed
Harvey 1939
-
- Harvey A. The mechanism of action of quinine in myotonia and myasthenia. JAMA 1939;112:1562‐3.
Haskell 1997
-
- Haskell SG, Fiebach NH. Clinical epidemiology of nocturnal leg cramps in male veterans. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 1997;313(4):210‐14. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jansen 1990
-
- Jansen PH, Joosten EM, Vingerhoets HM. Muscle cramp: main theories as to aetiology. European Archives of Psychiatry & Neurological Sciences 1990;239(5):337‐42. - PubMed
Katzberg 2010
-
- Katzberg HD, Khan AH, So YT. Assessment: symptomatic treatment for muscle cramps (an evidence‐based review). Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2010;74(8):691–6. - PubMed
Kaufman 1993
-
- Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Johannes CB, Sandler A, Harmon D, Stolley PD, et al. Acute thrombocytopenic purpura in relation to the use of drugs. Blood 1993;82(9):2714‐8. - PubMed
Khajehdehi 2001
-
- Khajehdehi P, Mojerlou M, Behzadi S, Rais‐Jalali GA. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of supplementary vitamins E, C and their combination for treatment of haemodialysis cramps. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2001;16(7):1448‐51. - PubMed
Knower 2003
-
- Knower MT, Bowton DL, Owen J, Dunagan DP. Quinine‐induced disseminated intravascular coagulation: case report and review of the literature. Intensive Care Medicine 2003;29(6):1007‐11. - PubMed
Krishna 1996
-
- Krishna S, White NJ. Pharmacokinetics of quinine, chloroquine and amodiaquine. Clinical implications. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 1996;30(4):263‐99. - PubMed
Langford 2003
Latta 1989
-
- Latta D, Turner E. An alternative to quinine in nocturnal leg cramps. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1989;45:833‐7.
Layzer 1994
-
- Layzer RB. The origin of muscle fasciculations and cramps. Muscle and Nerve 1994;17(11):1243‐9. - PubMed
Mackie 1995
Maguire 1993
-
- Maguire RB, Stroncek DF, Campbell AC. Recurrent pancytopenia, coagulopathy, and renal failure associated with multiple quinine‐dependent antibodies. Annals of Internal Medicine 1993;119(3):215‐17. - PubMed
Man‐Son‐Hing 1995
Man‐Son‐Hing 1998
Mandal 1995
-
- Mandal AK, Abernathy T, Nelluri SN, Stitzel V. Is quinine effective and safe in leg cramps?. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1995;35(6):588‐93. - PubMed
Martindale 1996
-
- Martindale W, Westcott W. In: Martindale W, Westcott W editor(s). The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 1st Edition. London: Royal Pharmaceutical Society, 1996:474‐77.
McDonald 1997
-
- McDonald SP, Shanahan EM, Thomas AC, Roxby DJ, Beroukas D, Barbara JA. Quinine‐induced hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clinical Nephrology 1997;47(6):397‐400. - PubMed
McGee 1990
-
- McGee SR. Muscle cramps. Archives of Internal Medicine 1990;150(3):511‐18. - PubMed
McGready 2001
-
- McGready R, Cho T, Samuel, Villegas L, Brockman A, van Vugt M, et al. Randomized comparison of quinine‐clindamycin versus artesunate in the treatment of falciparum malaria in pregnancy. Transactions of The Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2001;95(6):651‐6. - PubMed
McGready 2002
-
- McGready R, Thwai KL, Cho T, Samuel, Looareesuwan S, White NJ, et al. The effects of quinine and chloroquine antimalarial treatments in the first trimester of pregnancy. Transactions of The Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2002;96(2):180‐4. - PubMed
McKinna 1966
-
- McKinna AJ. Quinine induced hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Canadian Journal of Ophthalmology 1966;1(4):261. - PubMed
Miller 2005
-
- Miller ER 3rd, Pastor‐Barriuso R, Dalal D, Riemersma RA, Appel LJ, Guallar E. Meta‐analysis: high‐dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all‐cause mortality. Annals of Internal Medicine 2005;142(1):37‐46. - PubMed
Miller TM 2005
-
- Miller TM, Layzer RB. Muscle cramps. Muscle and Nerve 2005;32(4):431‐42. - PubMed
Morgon 1971
-
- Morgon A, Charachon D, Brinquier N. Disorders of the auditory apparatus caused by embryopathy or foetopathy: prophylaxis and treatment. Acta Otolaryngology (Suppl) 1971;291:1‐27. - PubMed
Morton 2002
-
- Morton AP. Quinine‐induced disseminated intravascular coagulation and haemolytic‐uraemic syndrome. Medical Journal of Australia 2002;176(7):351. - PubMed
Moss 1940
-
- Moss HK, Herrmann LG. The use of quinine for relief of night cramps in the extremities. Journal of the American Medical Association 1940;115:1358‐9.
Mutual 2006
-
- Mutual Pharmaceutical Company. Quinine sulfate [package insert]. Philadelphia, PA: 2006. thomsonweb.esourcegroup.com/files/PI_0.pdf (accessed 2 February 2009).
Naylor 1994
-
- Naylor RJ, Young JB. A general population survey of leg cramps. Age and Ageing 1994;23(5):418‐20. - PubMed
Nicholson 1945
-
- Nicholson JH, Falk A. Night cramps in young men. New England Journal of Medicine 1945;233:556‐9.
Nishimura 1976
-
- Nishimura H, Tanimura T. Clinical Aspects of The Teratogenicity of Drugs. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica, 1976.
Nosten 2002
-
- Nosten F, McGready R, D'Alessandro U, Bonell A, Verhoeff F, Menendez C, et al. The effects of quinine and chloroquine antimalarial treatments in the first trimester of pregnancy. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine & Hygiene 2002;96:180‐4. - PubMed
Nosten 2006
-
- Nosten F, McGready R, d'Alessandro U, Bonell A, Verhoeff F, Menendez C, et al. Antimalarial drugs in pregnancy: a review. Current Drug Safety 2006;1:1‐15. - PubMed
Orton 2008
Pederson 1985
-
- Pedersen KE, Lysgaard Madsen J, Klitgaard NA, Kjaer K, Hvidt S. Effect of quinine on plasma digoxin concentration and renal digoxin clearance. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1985;218(2):229‐32. - PubMed
Peer 1983
-
- Peer G, Blum M, Aviram A. Relief of hemodialysis‐induced muscular cramps by nifedipine. Dialysis and Transplantation 1983;12:180‐1.
Phillips‐Howard 1996
-
- Phillips‐Howard PA, Wood D. The safety of antimalarial drugs in pregnancy. Drug Safety 1996;14(3):131‐45. - PubMed
Piola 2010
-
- Piola P, Nabasumba C, Turyakira E, Dhorda M, Lindegardh N, Nyehangane D, et al. Efficacy and safety of artemether‐lumefantrine compared with quinine in pregnant women with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria: an open‐label, randomised, non‐inferiority trial. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2010;10(11):762‐9. - PubMed
Prasad 2003
-
- Prasad RS, Kodali VR, Khuraijam GS, Cho M, Travers JP. Acute confusion and blindness from quinine toxicity. European Journal of Emergency Medicine 2003;10(4):353‐6. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roffe 2002
-
- Roffe C, Sills S, Crome P, Jones P. Randomised, cross‐over, placebo controlled trial of magnesium citrate in the treatment of chronic persistent leg cramps. Medical Science Monitor 2002;8(5):326‐30. - PubMed
Schneemann 2006
-
- Schneemann M. Quinine. In: Aronson JK editor(s). Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs. 15th Edition. New York: Elsevier Science, 2006:3002‐7.
White 2007
-
- White NJ. Cardiotoxicity of antimalarial drugs. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2007;7(8):549‐58. - PubMed
WHO 2010
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the treatment of malaria. 2nd Edition. Geneva: WHO Press, 2010.
Young 1993
References to other published versions of this review
El Tawil 2004
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

