The fast azimuthal integration Python library: pyFAI
- PMID: 25844080
- PMCID: PMC4379438
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600576715004306
The fast azimuthal integration Python library: pyFAI
Abstract
pyFAI is an open-source software package designed to perform azimuthal integration and, correspondingly, two-dimensional regrouping on area-detector frames for small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering experiments. It is written in Python (with binary submodules for improved performance), a language widely accepted and used by the scientific community today, which enables users to easily incorporate the pyFAI library into their processing pipeline. This article focuses on recent work, especially the ease of calibration, its accuracy and the execution speed for integration.
Keywords: GPU programming; Python; computer programs; data reduction; geometry calibration; image analysis; powder diffraction; small-angle X-ray scattering.
Figures
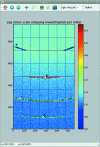
 ) calibrant on the Cristal beamline at Synchrotron Soleil taken at 18.57 keV on an Xpad S540 flat pixel detector tilted vertically by about 15°. This detector presents large (vertical) gaps between modules, explaining the incomplete arcs of rings a, b and d. Extracted control points are marked with dots, one colour per group (assigned to a letter), and the fitted iso-
) calibrant on the Cristal beamline at Synchrotron Soleil taken at 18.57 keV on an Xpad S540 flat pixel detector tilted vertically by about 15°. This detector presents large (vertical) gaps between modules, explaining the incomplete arcs of rings a, b and d. Extracted control points are marked with dots, one colour per group (assigned to a letter), and the fitted iso- contours are overlaid as dashed lines (red, orange and yellow coloured). The iso-
contours are overlaid as dashed lines (red, orange and yellow coloured). The iso- contour plot is not smooth because of gaps in the detector, explaining the incompleteness of some rings.
contour plot is not smooth because of gaps in the detector, explaining the incompleteness of some rings.


References
-
- Behnel, S., Bradshaw, R., Citro, C., Dalcin, L., Seljebotn, D. & Smith, K. (2011). Comput. Sci. Eng. 13, 31–39.
-
- Bonnin, A., Wright, J. P., Tucoulou, R. & Palancher, H. (2014). Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 084103.
-
- Borbely, A., Renversade, L., Kenesei, P. & Wright, J. (2014). J. Appl. Cryst. 47, 1042–1053.
-
- Boeecke, P. (2007). J. Appl. Cryst. 40, s423–s427.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
