Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of recurrence and progression in patients with high-grade pT1 bladder cancer
- PMID: 25844098
- PMCID: PMC4374998
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.2523
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of recurrence and progression in patients with high-grade pT1 bladder cancer
Abstract
Introduction: We investigated the value of the preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in predicting recurrence and progression of high-grade pT1 non-muscle-invasive tumour in patients with bladder cancer during a 5-year follow-up period.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed data of 1100 patients with bladder cancer; these patients underwent transurethral resection and were monitored at multiple centres from 2008 to 2013. In total, 166 consecutive and newly diagnosed patients with high-grade pT1 tumours were included in this study. The NLR was calculated by dividing the absolute neutrophil count by the absolute lymphocyte count.
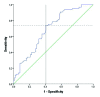
Results: Of the 166 patients, 152 were male. The patients were evaluated as two separate groups in terms of recurrence and progression. The mean follow-up period was 24.2 months (interquartile range 13.8-36.6 months). A statistically significant difference was found between recurrence and tumour size (p = 0.001), number of tumours (p < 0.001), NLR (p < 0.001), and smoking (p = 0.007). No statistically significant correlation was found between NLR and progression. According to receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, the optimum cut-off value for the NLR was ≥2.43 (74% sensitivity, 60% specificity, p < 0.001; area under the curve [AUC] 0.687, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.607-0.767). Multivariate logistic regression analysis determined that the following factors were independent predictors of recurrence in patients with high-grade pT1 non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: tumour number (OR 5.32, 95% CI 2.10-12.90), NLR of ≥2.43 (OR 2.587; 95% CI 1.156-5.789), and smoking (OR 4.17, 95% CI 1.31-13.21).
Conclusion: A high preoperative NLR may play an important role in predicting recurrence of superficial transitional cell type high-grade pT1 bladder tumours. Prospective studies are required to validate the role of NLR as a prognostic marker in high-grade pT1 bladder tumours.
Figures
References
-
- Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol. 2006;49:466–5. discussion 465–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources