Molecular breeding of thermo-sensitive genic male sterile (TGMS) lines of rice for blast resistance using Pi2 gene
- PMID: 25844116
- PMCID: PMC4384964
- DOI: 10.1186/s12284-015-0048-3
Molecular breeding of thermo-sensitive genic male sterile (TGMS) lines of rice for blast resistance using Pi2 gene
Abstract
Background: Blast disease caused by the fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae is one of the big problems in rice production in China, especially for high yield hybrid varieties made from a two-line system in which thermo-sensitive genic male sterile (TGMS) lines are used. In this study, we report the introgression of a rice blast resistance gene Pi2 from VE6219 into C815S, an elite rice TGMS line, leading to the development of blast resistant TGMS lines through marker assisted selection (MAS) and phenotypic selection approaches.
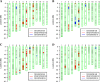
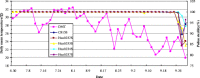
Results: Four new TGMS lines with blast resistance gene Pi2 were developed from C815S (an elite TGMS line susceptible to the blast, used as recurrent parent) and VE6219 (a blast resistant line harboring Pi2, used as donor parent). The pathogenicity assays inoculated with 53 blast prevalent isolates in glasshouse showed that the blast resistant frequency of the four TGMS lines was 94.3%-98.1% that is equivalent to blast resistant donor parent VE6219. The field evaluation of the new lines and hybrids made from them at a blast epidemic site also showed high resistant levels against the blast. The genetic background of the newly developed TGMS lines were examined using a whole-genome single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array (RICE6K) that turned out more than 83% of the genomic markers were derived from the recurrent parent. The critical temperature points of fertility-sterility alteration of the new TGMS lines were between 22°C and 23°C of daily mean temperature, which is similar to that of C815S. The complete male sterility under natural growth conditions at Wuhan last more than 80 days. Their agronomic and grain quality traits meet the requirement for two-line hybrid rice production.
Conclusions: The broad-spectrum and durable rice blast resistant gene Pi2 was introgressed into the elite TGMS line C815S background. The newly developed TGMS lines can be practically used for two-line hybrid rice breeding and must play an important role in sustainable rice production in China.
Keywords: Marker-assisted selection; Pi2; Rice blast resistance; TGMS line; Two-line hybrid rice.
Figures


References
-
- Bonman JM, Dedios TIV, Khin MM. Physiological Specialization of Pyricularia-Oryzae in the Philippines. Plant Dis. 1986;70(8):767–769. doi: 10.1094/PD-70-767. - DOI
-
- Chen HQ, Chen ZX, Ni S, Zuo SM, Pan XB, Zhu XD. Pyramiding three genes with resistance to blast by marker assisted selection to improve rice blast resistance of Jin 23B (in Chinese with English summary) Chinese J Rice Sci. 2008;22(1):23–27.
-
- Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB. A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 1983;1(4):19–21. doi: 10.1007/BF02712670. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

