Factors of the HIV Transmission in Men Who Have Sex with Men in Suizhou City from 2009 to 2013
- PMID: 25844172
- PMCID: PMC4380911
- DOI: 10.1002/sm2.55
Factors of the HIV Transmission in Men Who Have Sex with Men in Suizhou City from 2009 to 2013
Abstract
Introduction: The primary transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has been recently changing worldwide. In China, HIV transmission through heterosexual contact remains the predominant mode, but the prevalence of men who have sex with men (MSM) has been increasing.
Aim: This article investigated the overall epidemic trend and associated high-risk behavior among MSM in Suizhou City and explored the government's responses to the epidemic.
Methods: We conducted yearly cross-sectional behavioral surveillance surveys among MSM in Suizhou City from 2009 to 2013. Participation was anonymous and self-completed. Recruitment methods were consistently applied in each survey.
Main outcome measures: Semi-structured questionnaire surveys and yearly work summaries were conducted.
Results: Most of the MSM groups in Suizhou City were young adults (P < 0.05), well educated (P < 0.05), and married (P < 0.05). Two years after our interventions, we found an increasing trend of condom use during anal sex (P < 0.05), as well as commercial sex trade (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: HIV continues to spread rapidly among MSM in Suizhou City. The high-risk behavior among MSM remains a hindrance to HIV prevention. Innovative intervention approaches are essential for HIV surveillance and prevention among MSM in Suizhou City. Yang F, Shi X, He W, Wu S, Wang J, Zhao K, Yuan H, Martin K, and Zhang H. Factors of the HIV transmission in men who have sex with men in Suizhou City from 2009 to 2013. Sex Med 2015;3:24-31.
Keywords: Anal Intercourse with Male; Condom Usage; HIV; High-risk behavior; Intervention; MSM.
Figures
References
-
- Chow EP, Wilson DP, Zhang J, Jing J, Zhang L. Human immunodeficiency virus prevalence is increasing among men who have sex with men in China: Findings from a review and meta-analysis. Sex Transm Dis. 2011;38:845–857. - PubMed
-
- Wang N. Some new trends of HIV/AIDS epidemic in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2010;31:1205–1209. - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2012, Switzerland. Available at: http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2012/20121120_UNAIDS_Global... (accessed January 13, 2015)
-
- Shao B, Li Y, Yu L, Wang K, Chang M, Wang B, Wang F. The HIV/AIDS epidemic characteristics in a northeast province of China–men who have sex with men have made a tremendous contribution to the growth of the HIV epidemic. J Infect. 2014;68:273–280. - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS. Global AIDS progress report, country progress report 2012, Australia. Available at: http://www.unaids.org/en/dataanalysis/knowyourresponse/countryprogressre... (accessed January 13, 2015)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

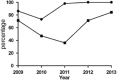
 The anal intercourse with male rate in the last 6 months (2009–2013).
The anal intercourse with male rate in the last 6 months (2009–2013).  The rate of use of condom during anal intercourse with male in the last 6 months (2009–2013).
The rate of use of condom during anal intercourse with male in the last 6 months (2009–2013).