Oral Appliance Treatment Response and Polysomnographic Phenotypes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- PMID: 25845897
- PMCID: PMC4513263
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.4934
Oral Appliance Treatment Response and Polysomnographic Phenotypes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
Study objectives: Mandibular advancement splints (MAS) are an effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA); however, therapeutic response is variable. Younger age, female gender, less obesity, and milder and supine-dependent OSA have variably been associated with treatment success in relatively small samples. Our objective was to utilize a large cohort of MAS treated patients (1) to compare efficacy across patients with different phenotypes of OSA and (2) to assess demographic, anthropometric, and polysomnography variables as treatment response predictors.
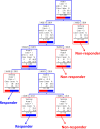
Methods: Retrospective analysis of MAS-treated patients participating in clinical trials in sleep centers in Sydney, Australia between years 2000-2013. All studies used equivalent customized two-piece MAS devices and treatment protocols. Treatment response was defined as (1) apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) < 5/h, (2) AHI < 10/h and ≥ 50% reduction, and (3) ≥ 50% AHI reduction.
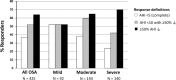
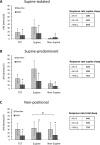
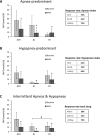
Results: A total of 425 patients (109 female) were included (age 51.2 ± 10.9 years, BMI 29.2 ± 5.0 kg/m2). MAS reduced AHI by 50.3% ± 50.7% across the group. Supine-predominant OSA patients had lower treatment response rates than non-positional OSA (e.g., 36% vs. 59% for AHI < 10/h). REM-predominant OSA showed a lower response rate than either NREM or non-stage dependent OSA. In prediction modelling, age, baseline AHI, and anthropometric variables were predictive of MAS treatment outcome but not OSA phenotype. Gender was not associated with treatment outcome.
Conclusion: Lower MAS treatment response rates were observed in supine and REM sleep. In a large sample, we confirm that demographic, anthropometric, and polysomnographic data only weakly inform about MAS efficacy, supporting the need for alternative objective prediction methods to reliably select patients for MAS treatment.
Keywords: obstructive sleep apnea; oral appliance; polysomnography; treatment response.
© 2015 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Marklund M, Verbraecken J, Randerath W. Non-CPAP therapies in obstructive sleep apnoea: mandibular advancement device therapy. Eur Respir J. 2012;39:1241–7. - PubMed
-
- Mehta A, Qian J, Petocz P, Darendeliler MA, Cistulli PA. A randomized, controlled study of a mandibular advancement splint for obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1457–61. - PubMed
-
- Kushida CA, Littner MR, Morgenthaler T, et al. Practice parameters for the indications for polysomnography and related procedures: an update for 2005. Sleep. 2005;28:499–521. - PubMed
-
- Phillips CL, Grunstein RR, Darendeliler MA, et al. Health outcomes of continuous positive airway pressure versus oral appliance treatment for obstructive sleep apnea: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:879–87. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

