Remission of systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity with regulatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-35 in Murphy Roths Large (MRL)/lpr mice
- PMID: 25845911
- PMCID: PMC4516441
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12639
Remission of systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity with regulatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-35 in Murphy Roths Large (MRL)/lpr mice
Abstract
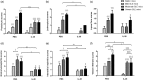
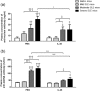
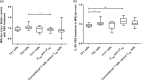
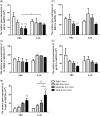
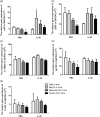
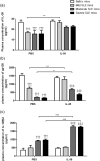
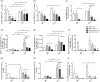
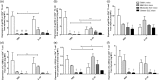
The immunological mechanisms mediated by regulatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-35 are unclear in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We investigated the frequency of CD4(+) CD25(+) forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3)(+) regulatory T (Treg ) and IL-10(+) regulatory B (Breg ) cells and related immunoregulatory mechanisms in a female Murphy Roths Large (MRL)/lpr mouse model of spontaneous lupus-like disease, with or without IL-35 treatment. A remission of histopathology characteristics of lupus flare and nephritis was observed in the MRL/lpr mice upon IL-35 treatment. Accordingly, IL-35 and IL-35 receptor subunits (gp130 and IL-12Rβ2) and cytokines of MRL/lpr and BALB/c mice (normal controls) were measured. The increased anti-inflammatory cytokines and decreased proinflammatory cytokines were possibly associated with the restoration of Treg and Breg frequency in MRL/lpr mice with IL-35 treatment, compared to phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) treatment. mRNA expressions of Treg -related FoxP3, IL-35 subunit (p35 and EBI3) and soluble IL-35 receptor subunit (gp130 and IL12Rβ2) in splenic cells were up-regulated significantly in IL-35-treated mice. Compared with the PBS treatment group, IL-35-treated MRL/lpr mice showed an up-regulation of Treg -related genes and the activation of IL-35-related intracellular Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signal pathways, thereby indicating the immunoregulatory role of IL-35 in SLE. These in vivo findings may provide a biochemical basis for further investigation of the regulatory mechanisms of IL-35 for the treatment of autoimmune-mediated inflammation.
Keywords: cytokines; interleukin-35; regulatory B cells; regulatory T cells; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2015 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
References
-
- Van Parijs L, Abbas AK, et al. Homeostasis and self-tolerance in the immune system: turning lymphocytes off. Science. 1998;280:243–8. - PubMed
-
- Kappler JW, Roehm N, Marrack P. T cell tolerance by clonal elimination in the thymus. Cell. 1987;49:273–80. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells: key controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell. 2000;101:455–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

