Air pollution exposure: a novel environmental risk factor for interstitial lung disease?
- PMID: 25846532
- PMCID: PMC4388120
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.14-1299
Air pollution exposure: a novel environmental risk factor for interstitial lung disease?
Abstract
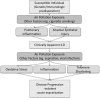
Air pollution exposure is a well-established risk factor for several adverse respiratory outcomes, including airways diseases and lung cancer. Few studies have investigated the relationship between air pollution and interstitial lung disease (ILD) despite many forms of ILD arising from environmental exposures. There are potential mechanisms by which air pollution could cause, exacerbate, or accelerate the progression of certain forms of ILD via pulmonary and systemic inflammation as well as oxidative stress. This article will review the current epidemiologic and translational data supporting the plausibility of this relationship and propose a new conceptual framework for characterizing novel environmental risk factors for these forms of lung disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The effect of air pollution in diffuse interstitial lung disease].Rev Mal Respir. 2020 May;37(5):389-398. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2020.02.015. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Rev Mal Respir. 2020. PMID: 32278507 Review. French.
-
The association between air pollution and the severity at diagnosis and progression of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: results from the retrospective ScleroPol study.Respir Res. 2023 Jun 8;24(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02463-w. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37291562 Free PMC article.
-
Air Pollution and Interstitial Lung Diseases: Defining Epigenomic Effects.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Nov 1;202(9):1217-1224. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202003-0836PP. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32569479 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Fibrotic interstitial lung diseases and air pollution: a systematic literature review.Eur Respir Rev. 2020 Aug 18;29(157):200093. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0093-2020. Print 2020 Sep 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2020. PMID: 32817115 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality and Morbidity Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Low-Level PM2.5, BC, NO2, and O3: An Analysis of European Cohorts in the ELAPSE Project.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2021 Sep;2021(208):1-127. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2021. PMID: 36106702 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Morbidity, Disability and Death Rates of The Population Due to Malignant Neoplasms in Uralsk City in The Republic of Kazakhstan.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016 Dec 1;17(12):5159-5164. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2016.17.12.5159. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016. PMID: 28124881 Free PMC article.
-
The Respiratory Risks of Ambient/Outdoor Air Pollution.Clin Chest Med. 2020 Dec;41(4):809-824. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2020.08.013. Clin Chest Med. 2020. PMID: 33153697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Air Pollution and Weather on Dry Eye.J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 20;9(11):3740. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113740. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33233863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outdoor Air Pollution and Childhood Respiratory Disease: The Role of Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 22;24(5):4345. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054345. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and systemic sclerosis: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jul;78(14):5527-5542. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03874-y. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34145462 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pinkerton KE. A Critical Review of the Particulate Matter Toxicology Literature for Senate Bill 25 Review of the Particulate Matter Standard. Sacramento, CA: California Environmental Protection Agency, Air Resources Board, Research Division; 2002:1-93.
-
- Ayyagari VN, Januszkiewicz A, Nath J. Pro-inflammatory responses of human bronchial epithelial cells to acute nitrogen dioxide exposure. Toxicology. 2004;197(2):149-164. - PubMed
-
- Solomon C, Christian DL, Chen LL, et al. Effect of serial-day exposure to nitrogen dioxide on airway and blood leukocytes and lymphocyte subsets. Eur Respir J. 2000;15(5):922-928. - PubMed
-
- Frampton MW, Boscia J, Roberts NJ, Jr, et al. Nitrogen dioxide exposure: effects on airway and blood cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002;282(1):L155-L165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

