Characterizing and Overriding the Structural Mechanism of the Quizartinib-Resistant FLT3 "Gatekeeper" F691L Mutation with PLX3397
- PMID: 25847190
- PMCID: PMC4522415
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0060
Characterizing and Overriding the Structural Mechanism of the Quizartinib-Resistant FLT3 "Gatekeeper" F691L Mutation with PLX3397
Abstract
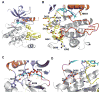
Tyrosine kinase domain mutations are a common cause of acquired clinical resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) used to treat cancer, including the FLT3 inhibitor quizartinib. Mutation of kinase "gatekeeper" residues, which control access to an allosteric pocket adjacent to the ATP-binding site, has been frequently implicated in TKI resistance. The molecular underpinnings of gatekeeper mutation-mediated resistance are incompletely understood. We report the first cocrystal structure of FLT3 with the TKI quizartinib, which demonstrates that quizartinib binding relies on essential edge-to-face aromatic interactions with the gatekeeper F691 residue, and F830 within the highly conserved Asp-Phe-Gly motif in the activation loop. This reliance makes quizartinib critically vulnerable to gatekeeper and activation loop substitutions while minimizing the impact of mutations elsewhere. Moreover, we identify PLX3397, a novel FLT3 inhibitor that retains activity against the F691L mutant due to a binding mode that depends less vitally on specific interactions with the gatekeeper position.
Significance: We report the first cocrystal structure of FLT3 with a kinase inhibitor, elucidating the structural mechanism of resistance due to the gatekeeper F691L mutation. PLX3397 is a novel FLT3 inhibitor with in vitro activity against this mutation but is vulnerable to kinase domain mutations in the FLT3 activation loop.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: C.C.S and A.P. (research funding associated with conduct of a clinical trial, Plexxikon); N.P.S. (research funding associated with the conduct of clinical trials, ARIAD Pharmaceuticals, Ambit Biosciences; research funding, Plexxikon, Daiichi-Sankyo). C.Z., Y.Z., R.S., G.T., H.C., B.P., E.A.B., B.M., W.S., P.N.I, M.H.L, H.H., G.H., B.L.W. and G.B. are employees of Plexxikon, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Shah NP, Nicoll JM, Nagar B, Gorre ME, Paquette RL, Kuriyan J, et al. Multiple BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations confer polyclonal resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571) in chronic phase and blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:117–25. - PubMed
-
- Cools J, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, Stover EH, Legare RD, Cortes J, et al. A tyrosine kinase created by fusion of the PDGFRA and FIP1L1 genes as a therapeutic target of imatinib in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1201–14. - PubMed
-
- Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, Ueno T, Takashima J, Nakajima T, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1734–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

