Upregulation of neuroglobin expression and changes in serum redox indices in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion
- PMID: 25847303
- PMCID: PMC4464340
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3593
Upregulation of neuroglobin expression and changes in serum redox indices in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion
Abstract
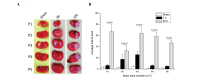
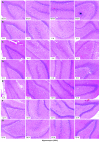
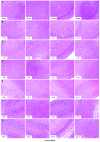
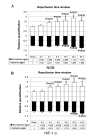
Neuroglobin (NGB) is a recently identified protein, which is localized in the neurons and retinal cells of the central and peripheral nervous systems in vertebrates. It is hypothesized to function as a scavenger for reactive oxygen species, or as a stress-responsive sensor for signal transduction in hypoxic-ischemic brain insults. However, the mechanism underlying the physiological function of this protein remains to be elucidated. In the present study, the profiling of changes in the serum redox index of morphological features of the hippocampus and cortex, and of the expression of NGB and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), are described in a rat middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model. The necrotic zone of the rat neural tissues increased in size with increasing reperfusion time, and different brain slices exhibited necrosis in different regions. The number of NGB-positive hippocampal and cortical cells, as well as NGB and HIF-1α transcript and protein levels in the ischemic cortex, increased with increasing reperfusion time. NGB and HIF-1α mRNA and protein levels peaked in the group that received reperfusion at 32 h after MCAO. These findings indicated that HIF-1α may be involved in ischemic pathology in an MCAO model and that NGB expression may be upregulated. Serum superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity decreased and serum malondialdehyde (MDA) levels increased with increasing reperfusion time, indicating that the redox potential increased following MCAO. Serum SOD and MDA measurements may, therefore, be useful as biomarkers for the early detection of ischemic injury in a clinical setting.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroglobin up-regulation after ischaemic pre-conditioning in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion.Brain Inj. 2015;29(5):651-7. doi: 10.3109/02699052.2014.1002004. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Brain Inj. 2015. PMID: 25625519
-
Increased neuroglobin levels in the cerebral cortex and serum after ischemia-reperfusion insults.Brain Res. 2006 Mar 17;1078(1):219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.01.064. Epub 2006 Feb 21. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16492379
-
Does neuroglobin protect neurons from ischemic insult? A quantitative investigation of neuroglobin expression following transient MCAo in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Brain Res. 2006 Apr 26;1085(1):19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.02.040. Epub 2006 May 2. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16647691
-
Hypoxia/ischemia and the regulation of neuroglobin and cytoglobin expression.IUBMB Life. 2004 Nov-Dec;56(11-12):681-7. doi: 10.1080/15216540500037406. IUBMB Life. 2004. PMID: 15804832 Review.
-
Neuroglobin and friends.J Mol Recognit. 2017 Dec;30(12). doi: 10.1002/jmr.2654. Epub 2017 Jul 14. J Mol Recognit. 2017. PMID: 28707399 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Hemin on Brain Alterations and Neuroglobin Expression in Water Immersion Restraint Stressed Rats.Scientifica (Cairo). 2016;2016:7825396. doi: 10.1155/2016/7825396. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Scientifica (Cairo). 2016. PMID: 27073715 Free PMC article.
-
Protection by Neuroglobin Expression in Brain Pathologies.Front Neurol. 2016 Sep 12;7:146. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00146. eCollection 2016. Front Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27672379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang L, Li LH, Qu Y, Mu DZ. Neuroglobin and hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2008;10:265–268. In Chinese. - PubMed
-
- Zhang CG, Li L, Deng MY, Xie F. Coding region cDNA sequence cloning of rat neuroglobin gene, its polymorphism feature and tissue expression profile analysis. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2001;28:997–1001. In Chinese. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

