Accuracy of multiecho magnitude-based MRI (M-MRI) for estimation of hepatic proton density fat fraction (PDFF) in children
- PMID: 25847512
- PMCID: PMC4592685
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.24888
Accuracy of multiecho magnitude-based MRI (M-MRI) for estimation of hepatic proton density fat fraction (PDFF) in children
Abstract
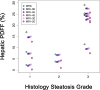
Purpose: To assess accuracy of magnitude-based magnetic resonance imaging (M-MRI) in children to estimate hepatic proton density fat fraction (PDFF) using two to six echoes, with magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) -measured PDFF as a reference standard.
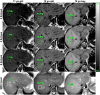
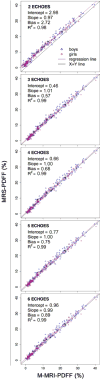
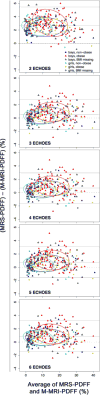
Methods: This was an IRB-approved, HIPAA-compliant, single-center, cross-sectional, retrospective analysis of data collected prospectively between 2008 and 2013 in children with known or suspected nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Two hundred eighty-six children (8-20 [mean 14.2 ± 2.5] years; 182 boys) underwent same-day MRS and M-MRI. Unenhanced two-dimensional axial spoiled gradient-recalled-echo images at six echo times were obtained at 3T after a single low-flip-angle (10°) excitation with ≥ 120-ms recovery time. Hepatic PDFF was estimated using the first two, three, four, five, and all six echoes. For each number of echoes, accuracy of M-MRI to estimate PDFF was assessed by linear regression with MRS-PDFF as reference standard. Accuracy metrics were regression intercept, slope, average bias, and R(2) .
Results: MRS-PDFF ranged from 0.2-40.4% (mean 13.1 ± 9.8%). Using three to six echoes, regression intercept, slope, and average bias were 0.46-0.96%, 0.99-1.01, and 0.57-0.89%, respectively. Using two echoes, these values were 2.98%, 0.97, and 2.72%, respectively. R(2) ranged 0.98-0.99 for all methods.
Conclusion: Using three to six echoes, M-MRI has high accuracy for hepatic PDFF estimation in children.
Keywords: MRI; MRS; NAFLD; PDFF; liver steatosis; proton density fat fraction.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bjermo H, Iggman D, Kullberg J, et al. Effects of n-6 PUFAs compared with SFAs on liver fat, lipoproteins, and inflammation in abdominal obesity: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95:1003–1012. - PubMed
-
- Maersk M, Belza A, Stodkilde-Jorgensen H, et al. Sucrose-sweetened beverages increase fat storage in the liver, muscle, and visceral fat depot: a 6-mo randomized intervention study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95:283–289. - PubMed
-
- Stein EA, Dufour R, Gagne C, et al. Apolipoprotein B synthesis inhibition with mipomersen in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to assess efficacy and safety as add-on therapy in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2012;126:2283–2292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

