Transcellular delivery of vesicular SOCS proteins from macrophages to epithelial cells blunts inflammatory signaling
- PMID: 25847945
- PMCID: PMC4419346
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20141675
Transcellular delivery of vesicular SOCS proteins from macrophages to epithelial cells blunts inflammatory signaling
Abstract
JAK-STAT signaling mediates the actions of numerous cytokines and growth factors, and its endogenous brake is the family of SOCS proteins. Consistent with their intracellular roles, SOCS proteins have never been identified in the extracellular space. Here we report that alveolar macrophages can secrete SOCS1 and -3 in exosomes and microparticles, respectively, for uptake by alveolar epithelial cells and subsequent inhibition of STAT activation. Secretion is tunable and occurs both in vitro and in vivo. SOCS secretion into lung lining fluid was diminished by cigarette smoking in humans and mice. Secretion and transcellular delivery of vesicular SOCS proteins thus represent a new model for the control of inflammatory signaling, which is subject to dysregulation during states of inflammation.
© 2015 Bourdonnay et al.
Figures
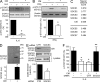
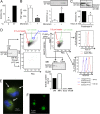
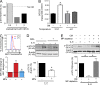

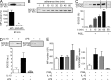


Comment in
-
Cytokines: Where there's smoke, there's fire.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 May;15(5):268-9. doi: 10.1038/nri3852. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25882244 No abstract available.
-
Special delivery: how macrophages get the message across.J Exp Med. 2015 May 4;212(5):598. doi: 10.1084/jem.2125insight1. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25941317 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akram K.M., Lomas N.J., Forsyth N.R., and Spiteri M.A.. 2014. Alveolar epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis display upregulation of TRAIL, DR4 and DR5 expression with simultaneous preferential over-expression of pro-apoptotic marker p53. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 7:552–564. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balter M.S., Toews G.B., and Peters-Golden M.. 1989. Multiple defects in arachidonate metabolism in alveolar macrophages from young asymptomatic smokers. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 114:662–673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

