Potentially fatal supramylohyoid sublingual epidermoid cyst
- PMID: 25848141
- PMCID: PMC4379300
- DOI: 10.1007/s12663-013-0594-4
Potentially fatal supramylohyoid sublingual epidermoid cyst
Abstract
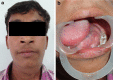
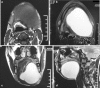
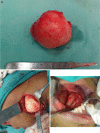
A case of chronic and slow growing massive lateral neck swelling is presented which gradually resulted in dysphagia to an extent that patient reported in emergency room. Clinical findings were indicative of a cystic swelling or a massive lipoma. Temporary decompression of the lesion was achieved by partially aspirating the contents of the cyst. Nature of aspirate and its microscopic and biochemical analysis excluded lipoma, vascular malformation and salivary phenomenon. The diagnosis tapered to developmental lateral neck cysts. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) revealed a massive cystic lesion in the left floor of mouth extending to the right lingual aspect of mandible and posteriorly to impinge on the medial wall of pharynx. A combined intraoral and extraoral approach was used to expose and excise the lesion in toto. Final histological diagnosis of the pathology was epidermoid cyst.
Keywords: Dermoid cyst; Dysphagia; FNAC; Lateral neck swelling.
Figures

References
-
- Marx R, Stern D. Oral and maxillofacial pathology. Chicago: Quintessence; 2003.
-
- Cortezzi W, de Albuquerque EB (1994) Secondarily infected epidermoid cyst in the floor of the mouth causing a life-threatening situation: report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 52:762–764 - PubMed
-
- New GB, Erich JB. Dermoid cysts of the head and neck. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1937;65:48–55.
-
- Taylor BW, Erich JB, Dockerty MB. Dermoids of the head and neck. Minn Med. 1966;49:1535–1540. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
