Management of renal cysts
- PMID: 25848184
- PMCID: PMC4376217
- DOI: 10.4293/JSLS.2014.00097
Management of renal cysts
Abstract
Background and objectives: Renal cysts have a high prevalence in the general population, and their estimated incidence increases with age. Renal cyst aspiration (usually with sclerotherapy) or open/laparoscopic decortication is a generally effective and safe method in the treatment of symptomatic simple renal cysts. The success rates of laparoscopic decortication and percutaneous aspiration-sclerotherapy were compared to assist in the decision making for the procedure.
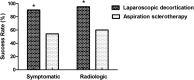
Methods: A total of 184 patients with symptomatic simple renal cysts were treated with either laparoscopic decortication in 149 cases or percutaneous aspiration-sclerotherapy in 35 cases. The follow-up period was approximately 35 months, and the symptomatic and radiologic success rates of the 2 techniques were compared retrospectively.
Results: Laparoscopic decortication was found to have high success rates, a low recurrence rate, and minimal morbidity. Percutaneous aspiration-sclerotherapy is an outpatient procedure with a minimally higher recurrence rate.
Conclusion: When a symptomatic cyst is encountered and treatment of the cyst is indicated, laparoscopic decortication is a more efficient method that offers better results than percutaneous aspiration-sclerotherapy.
Keywords: Laparoscopy; Renal cyst; Sclerotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Rane A. Laparoscopic management of symptomatic simple renal cysts. Int Urol Nephrol. 2004;36:5–9. - PubMed
-
- Skolarikos A, Laguna MP, de la Rosette JJ. Conservative and radiological management of simple renal cysts: a comprehensive review. BJU Int. 2012;110:170–178. - PubMed
-
- Hemal AK. Laparoscopic management of renal cystic disease. Urol Clin North Am. 2001;28:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Okeke AA, Mitchelmore AE, Keeley FX, Timoney AG. A comparison of aspiration and sclerotherapy with laparoscopic de-roofing in the management of symptomatic simple renal cysts. BJU Int. 2003;92:610–613. - PubMed
-
- Shao Q, Xu J, Adams T, et al. Comparison of aspiration-sclerotherapy versus laparoscopic decortication in management of symptomatic simple renal cysts. J Xray Sci Technol. 2013;21:419–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical